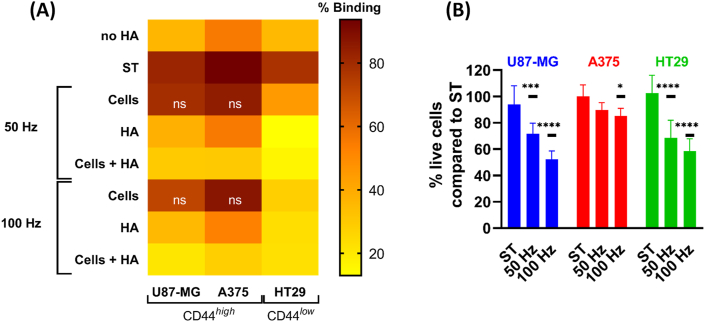
Fig. 4.
Oxidation of HA significantly reduces the binding of CD44+cancer cells. (A) CAP treatment of cancer cells (causing oxidation of surface receptors such as CD44) had little or no effect on their binding to HA-coated plates. However, oxidation of HA significantly reduced the binding of CD44high (U87-MG and A375) and CD44low (HT29) cells to the HA-coated plate. CAP treatment of both HA and CD44+ cells further reduced the binding. Wells coated only with BSA (no HA) served as negative controls. Mean values plotted express the percentage of binding of CD44+ cells to HA-coated plates for each condition. p ≤ 0.0001 for all samples compared to their corresponding sham-treated (ST) control, except when “ns” (not significant) is indicated. (B) Live cell count was done after CAP treatment, before transferring cells to the HA-coated plate. The percentage of live cells compared to the ST control is shown. Mean ± S.D. * = p ≤ 0.05; *** = p ≤ 0.001; **** = p ≤ 0.0001. In all cases, results were analyzed using the Dunnett post hoc test.