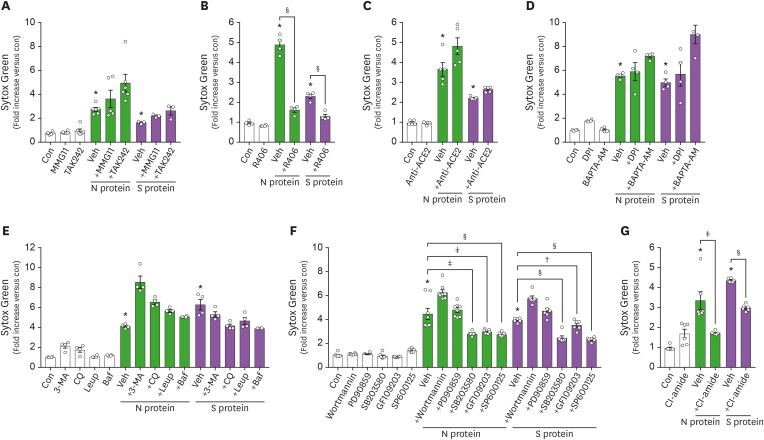
Figure 2. Neutrophils utilize a CLR-dependent pathway in viral protein-induced NET formation. (A-G) The effects of various inhibitors on viral protein-induced NET formation. Neutrophils were pre-treated with indicated inhibitors for 1 h, and further stimulated with viral proteins (100 nM) for 1 h. Veh; MMG11, a TLR2 inhibitor, 10 μM; TAK242, a TLR4 inhibitor, 10 μM; R406, a syk inhibitor, 1 μM; an anti-ACE2 Ab, 10 μg/ml; DPI, a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, 10 μM; BAPTA-AM, Ca2+ chelator, 100 μM; 3-MA, an autophagy sequestration inhibitor, 10 μM; CQ, an autophagosome degradation inhibitor, 10 μM; Leup, an autophagosome degradation inhibitor, 20 μM; Baf, an inhibitor for autophagosome-lysosome fusion, 10 μM; wortmannin, an inhibitor for PI3K, 10 μM; PD90859, an inhibitor for ERK, 10 μM; SB203580, an inhibitor for p38 MAPK, 10 μM; GF109203, a PKC inhibitor, 10 μM; SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, 10 μM; Cl-amide, a PAD4 inhibitor, 10 μM. Data are expressed as means±SEM.
Con, control; Veh, vehicle; 3-MA, 3-Methyladenine; Leup, leupeptin; CQ, chloroquine; Baf, bafilomycin.
*p<0.001 vs. Con; †p<0.05; ‡p<0.01; §p<0.001 vs. Veh.