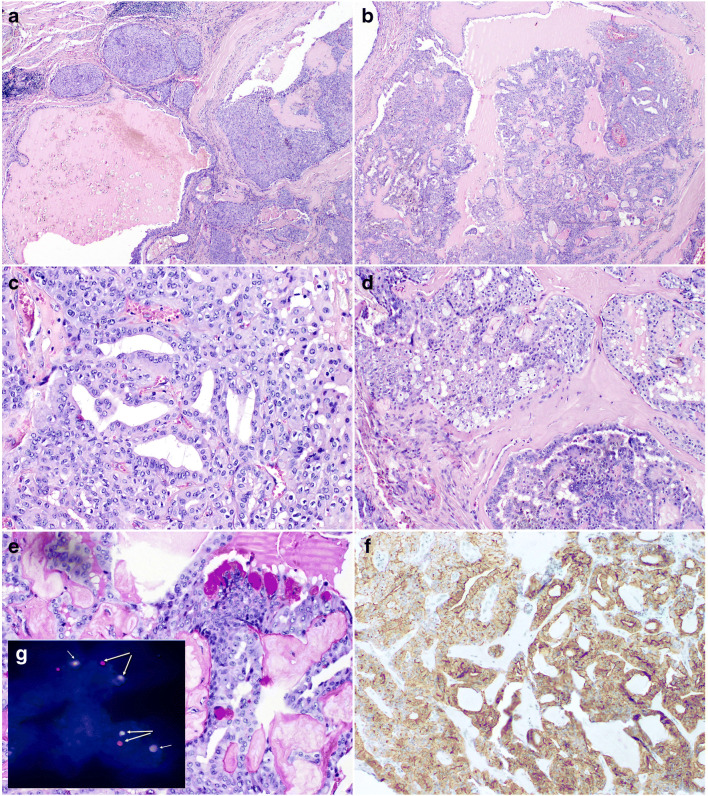
Fig. 1.
Intraductal carcinoma. a The unencapsulated tumor composed of variably sized cysts and nests with mainly intraductal proliferations The neoplastic nests contain epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and regular oval and round nuclei with conspicuous nucleoli (H&E × 20). b The cysts contained micropapillary structures, solid areas with irregular fenestrations or cribriform areas(H&E × 20). c–d The neoplastic nests contain epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and regular oval and round nuclei with conspicuous nucleoli (c H&E × 200; d H&E × 100). e Focal mucinous differentiation with PAS-positive vacuoles in the cytoplasm (H&E × 200). f Immunohistochemical staining showed strong membranous expression of ALK in 100% of cells (H&E × 200). g Fluorescence in situ hybridization with ALK Dual Color Break Apart FISH Probe. Nuclei with split red and green signals indicate ALK break (yellow arrows). Chromosome 2 with normal gene shows yellow signal (overlapping green and red and white arrows)