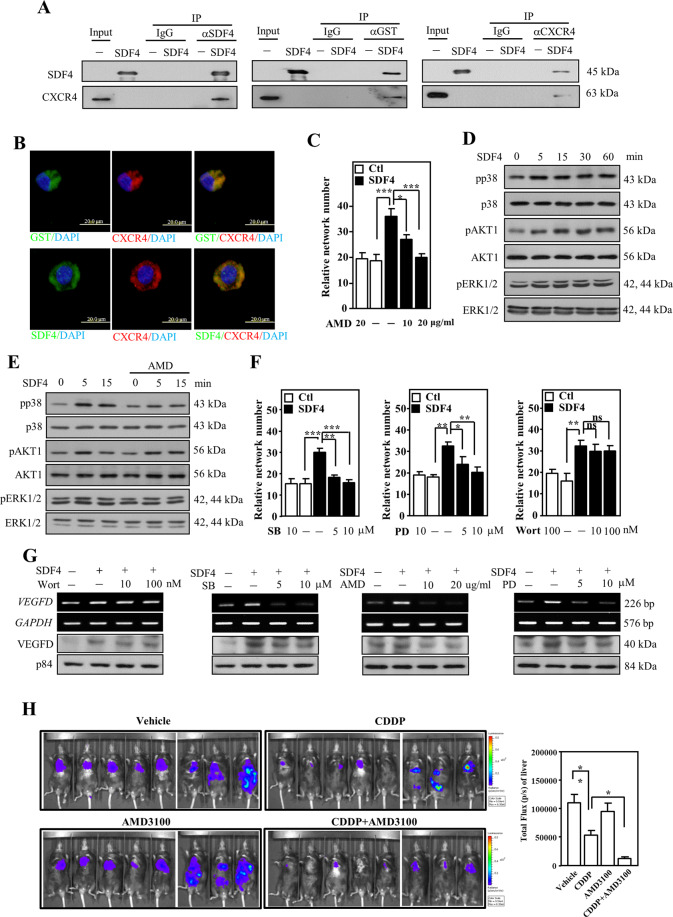
Fig. 5. SDF4 interacts with CXCR4 receptor to induce VEGFD expression for angiogenesis by phosphorylating ERK and p38 pathway proteins in endothelial cells.
A Cell membrane fractions were incubated with or without GST-SDF4, and then, a co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed with antibody against SDF4, GST or CXCR4. B An immunofluorescence assay was conducted to assess GST, SDF4, and CXCR4 signals. C Angiogenesis was assessed by counting the branched intersection number of SDF4-treated HUVECs with or without AMD3100 treatment as indicated. D, E The activity of AKT1, ERK1/2, and p38 in response to SDF4 (0.5 μg/ml) and with or without AMD3100 (20 μg/ml) treatment in the indicated time courses. F Angiogenesis was assessed by counting the branched intersection number of HUVECs treated with SDF4 and/or the indicated kinase inhibitors or SDF4 combined with pretreatment with increasing concentrations of wortmannin, PD98059 or SB203580. G VEGFD expression in response to various signaling inhibitors on SDF4-treated HUVECs. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. H LLC1-Luc2 cells were orthotopically inoculated into the lung of C57BL/6 mice. The experimental mice were treated with CDDP or AMD3100 as indication after inoculation with tumor cells. Representative in vivo bioluminescent images and total tumor flux of LLC1-Luc2-bearing mice in each group shown at 5th week. n = 8 per group. All data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. Differences among groups were analyzed with the one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.