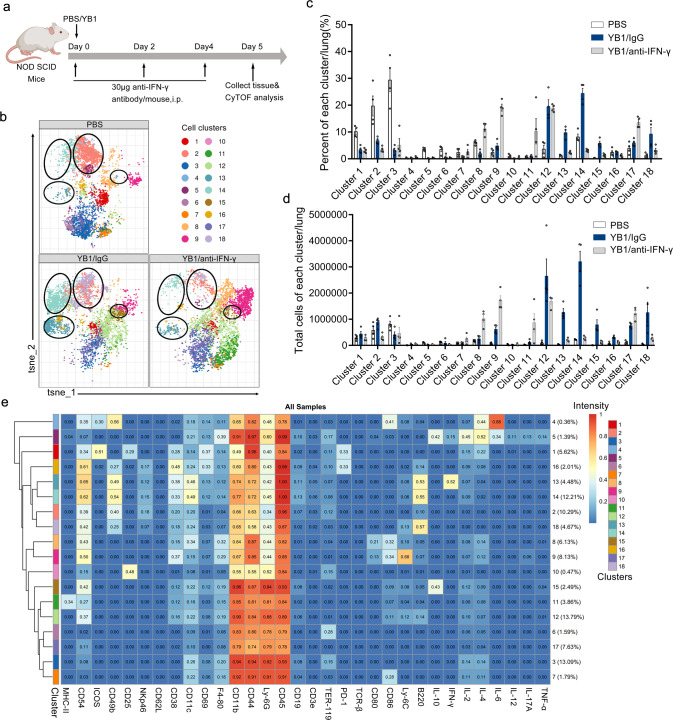
Fig. 5. IFN-γ promotes the accumulation of neutrophils and NK cells in the lung environment of NOD SCID mice after Salmonella YB1 treatment.
a Mice treatment timeline for CyTOF analysis. NOD SCID mice were divided into three groups treated with PBS, YB1 (YB1/IgG), or YB1 plus IFN-γ depletion antibody (YB1/anti-IFN-γ), respectively. All mice were killed on day 5 and lung-infiltrating immune cells were isolated and prepared for CyTOF analysis. b Representative t-SNE profile from each group of mice. Immune cell clusters 13, 14, 15, and 18 are highlighted by circles. c Percentage of each immune cell cluster per lung across samples (n = 4 per group). d Total cell number of each immune cell cluster per lung across samples (n = 4 per group). Immune cell clusters 13, 14, 15, and 18 were upregulated in the YB1 group compared to the other two control groups. c, d All data are presented as mean values ± SEM. e Characterization of each immune cell cluster. Based on the expressions of different phenotypic markers and cytokines, events acquired by CyTOF analysis of lung-infiltrating immune cells from NOD SCID mice with the three different treatments were merged for the t-SNE dimension reduction and PhenoGraph clustering analyses, and were divided into 18 immune cell clusters. Displayed one representative experiment of two independent experiments for all panels. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.