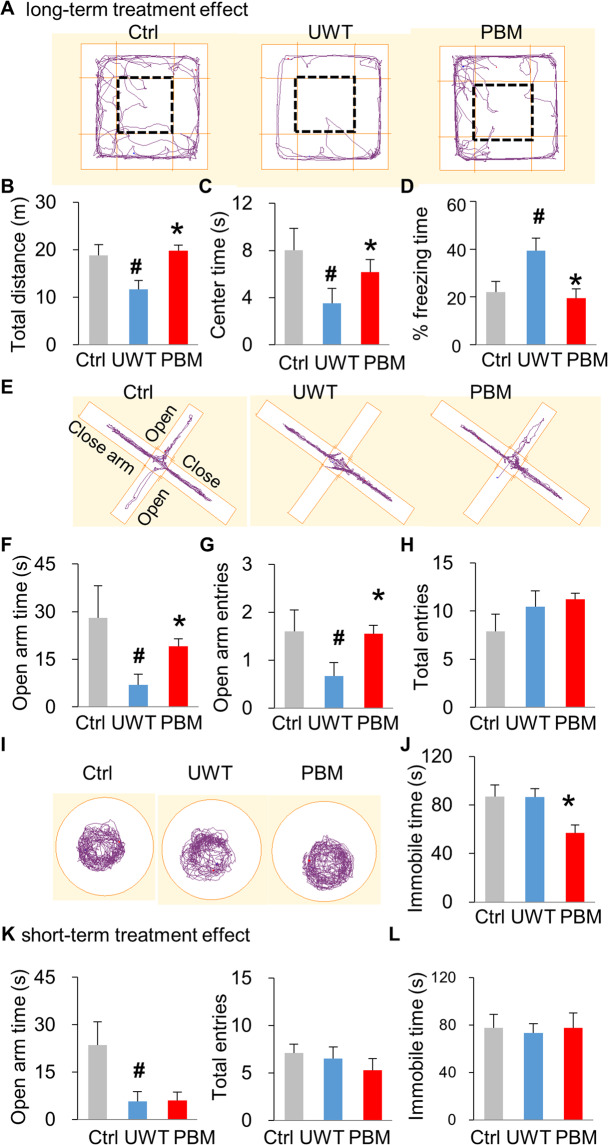
Fig. 2. PTSD-like comorbidities were prevented by PBM early interventions.
A–D PBM restores exploratory motor activity deficits in the open field arena test. A The apparatus and the representative exploration track for rats. The rectangle with a bold dashed line denotes the center zone. Three weeks post UWT, rats in UWT-group exhibited a significant reduction of total traveling distance in both the whole arena (B) and center zone (C), compared with the ctrl-group. PBM treatment restored exploratory activity for both the whole arena and center zone. D During the open field arena test, a higher percent of freezing was observed in UW-group rats but was reversed by PBM treatment. E–H PBM relieves anxiety-like behavior in the elevated plus maze test. E The apparatus for elevated plus maze. Rats in UWT-group spent less time exploring the open arms compared with ctrl-group rats. f PBM treatment increased the time visiting open arms compared to UWT-group rats. g Open arm entries mirrored the trend observed in time spent in open arms. H As a measurement control, all three groups had similar total arm entries. I, J PBM alleviates depression-like behavior in the forced swimming test. I The apparatus for forced swimming test. J PBM decreased the immobile time in PBM-group compared with the other two groups. n = 10, 9, 9 for ctrl, UWT, PBM-group, respectively. K, L A single dose of PBM treatment has no short-term treatment effect on either the elevated plus maze (K) and forced swimming test (L). To be noted, the anxiety-like, but not the depression-like behavior, was observed at 3 h post UWT. n = 8 each for ctrl-, UWT-, or PBM-group. * P < 0.05 versus UWT-group; #P < 0.05 versus ctrl-group.