Fig. 3. Cognitive dysfunction was prevented by PBM early interventions.
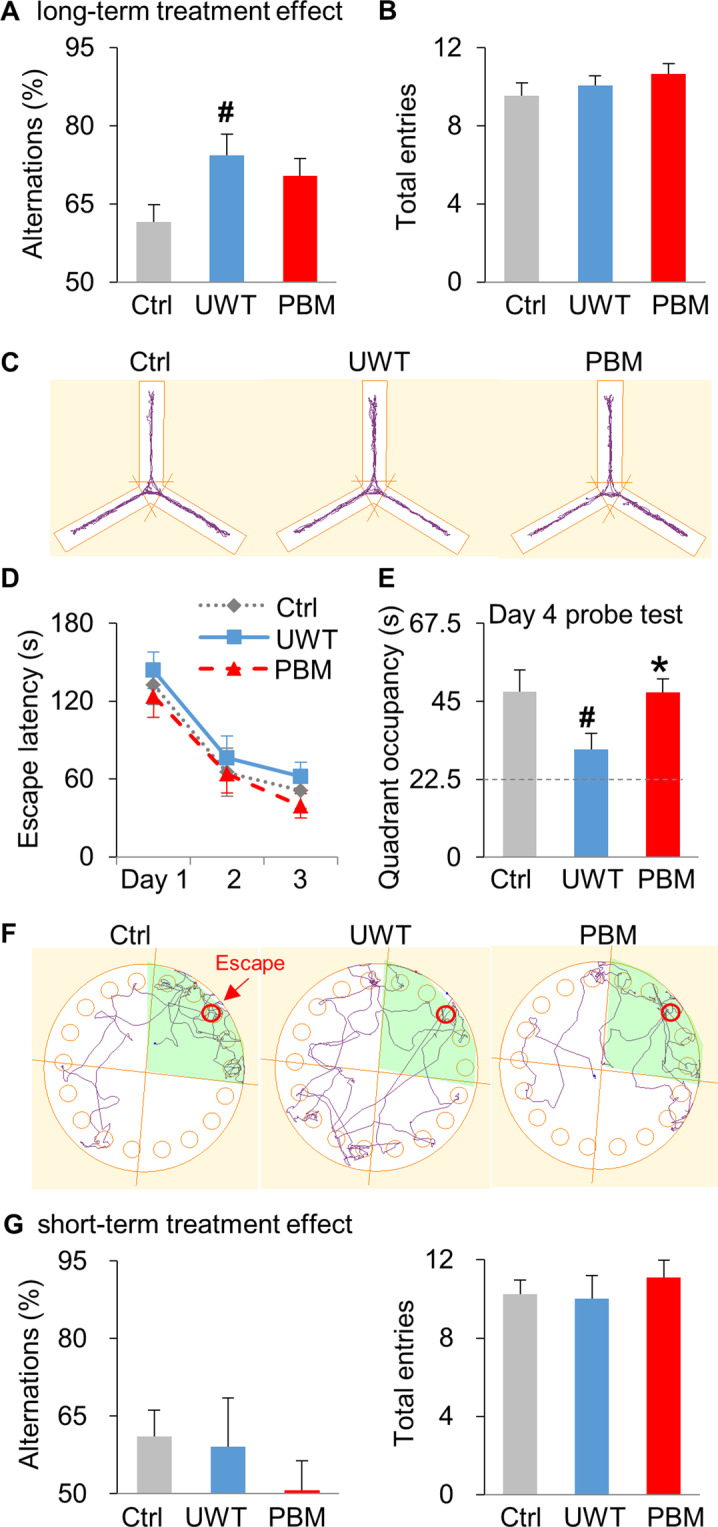
A–C UWT enhances working memory in the Y maze test, and PBM has no treatment effect. A Compared with the ctrl-group, UWT-group displayed better working memory, as shown by a higher percentage of alternation. B As a behavioral measurement control, all three groups had a similar number of total entries. C The apparatus and the representative exploration tracks for each group during Y maze testing. D–F PBM prevents long-term memory impairment in the Barnes maze test. D All three groups exhibited the same learning curve during the three days of training sessions (one trial/ day). E During the probe test session (90 s duration) at day 4, rats in UWT-group exhibited significantly decreased preference (22.5 s is random chance as labeled with dash line) for exploring the target quadrant where the escape chamber was previously located, compared with the other two groups. F The apparatus and the representative tracks on the probe test (day 4) for all three groups. Target quadrant is shaded, and the red circle denotes the location for the escape chamber. n = 10, 9, 9 for ctrl, UWT, PBM-group, respectively. G A single dose of PBM treatment has no short-term treatment effect on Y maze testing. n = 8 each for ctrl, UWT, or PBM-group. * P < 0.05 versus UWT-group; # P < 0.05 versus ctrl-group.
