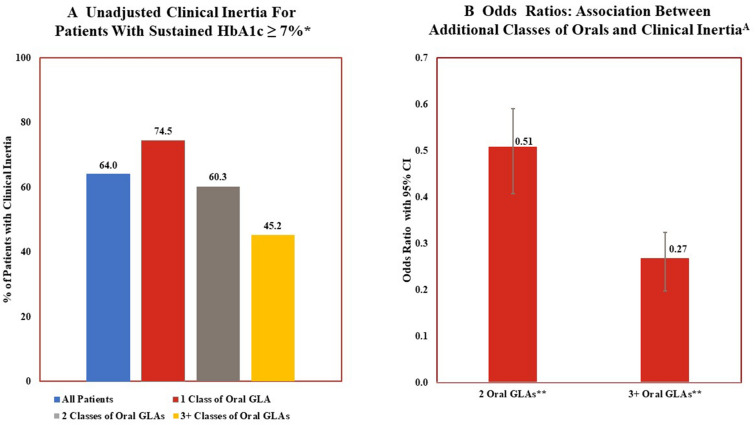
Fig. 4.
Clinical inertia and number of classes of oral glucose-lowering agents: descriptive statistics and multivariable analyses. *Unadjusted differences in results for patients based upon number of classes of oral GLAs prescribed at index date is statistically significant (P < 0.05). **Results from multivariable analyses that controls for age, sex, pre-period general health and length of time between HbA1c tests indicate significant lower odds of clinical inertia associated with being treated with 2 classes of oral GLAs or ≥ 3 classes of oral GLAs compared to patients treated with 1 class of oral GLA. Clinical inertia defined as no addition of other classes of GLAs