Figure 2.
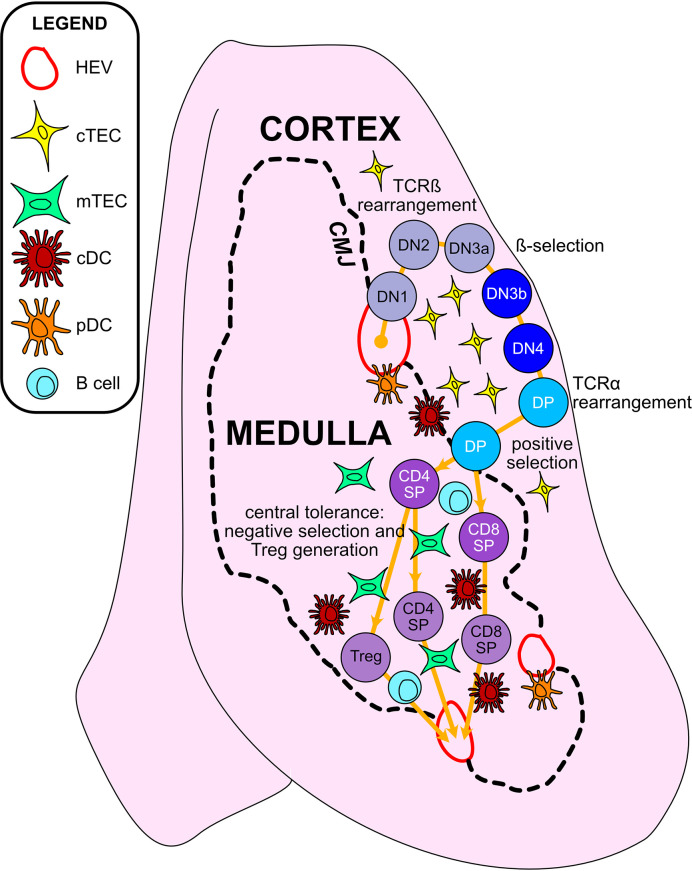
Thymic epithelial cells and hematopoietic antigen presenting cells provide essential signals to guide αβT cell maturation and the induction of central tolerance in the thymus. Cross-sectional view of a thymus lobe reveals cortical and medullary regions, through which thymocytes must travel in an orchestrated manner to encounter heterogeneous stromal cell subsets. Progenitor cells from the bone marrow migrate through the vasculature to seed the thymus at the cortico-medullary junction (CMJ). DN1-DN4 thymocytes require signals from cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs) to support their survival, proliferation, and T-lineage commitment. During the DN2-DN3 stages, TCRβ gene segments are recombined, and thymocytes that successfully express TCRβ and signal through the pre-TCR undergo proliferation and further differentiation through the process of β-selection. Subsequently, thymocytes upregulate CD4 and CD8 to become double-positive cells (DPs), which initiate TCRα gene rearrangements. DPs that successfully express a TCRαβ heterodimer are tested for reactivity with self-peptide MHC complexes presented by cTECs. Only those DPs that receive a TCR signal pass positive selection, enabling them to survive and further differentiate. Positively selected DPs transit from the cortex into the medulla. Along the way, some clones may be deleted in an early wave of negative selection in the cortex, driven by strong TCR reactivity to self-peptide MHC complexes displayed by dendritic cells (DCs). In the medulla, DPs downregulate either CD4 or CD8 to become single-positive thymocytes (CD8SP or CD4SP) and interact with medullary APCs to establish central tolerance to a broad array of self-antigens. Strong TCR signals, induced by self-antigens displayed by medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs), conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), or B cells result in either negative selection (apoptosis) or Treg diversion of the autoreactive T cell clones, enforcing central tolerance. SPs that survive these collective thymic selection processes emigrate from the thymus to join the peripheral T cell pool.