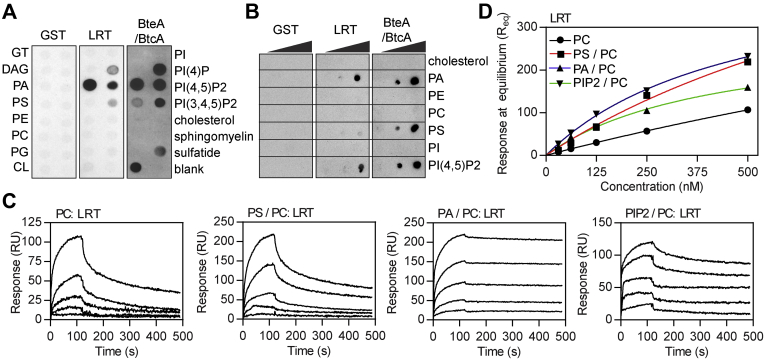
Figure 1.
Phospholipid binding by the N-terminal motif of Bordetella effector BteA.A and B, protein–lipid overlay assay. The recombinant GST-tagged N-terminal LRT domain (LRT) and full-length BteA (BteA/BtcA) protein of B. pertussis were incubated at 5 μg/ml with commercial (A) or home-made (B) lipid arrays. The binding was detected using an anti-GST antibody followed by chemiluminescence detection. Recombinant GST was used as a control. C, SPR real-time kinetics of LRT binding to lipid membranes. Serially diluted LRT protein (at 500, 250, 125, 62.5, and 31.25 nM concentrations) was injected in parallel over the neutravidin sensor chip coated with the immobilized liposomes (100 nm in diameter) containing PC, PS/PC (20:80), PA/PC (5:95), or PC/PIP2 (5:95) and left to associate (120 s) and dissociate (380 s) at constant flow rate of 30 μl/min. The sensograms show the representative binding curves from five independent “one-shot kinetic” experiments. D, SPR steady-state analysis of LRT binding to lipid vesicles. Serially diluted LRT protein was injected over the immobilized lipid vesicles to reach the SPR binding equilibrium, and the near-equilibrium values (Req) were plotted against LRT concentrations (P0). Solid lines represent binding isotherms determined by a nonlinear fitting of the data using the equation Req = Rmax/(1 + KD/P0). CL, cardiolipin; DAG, diacylglycerol; GT, triglyceride; GST, glutathione-S-transferase; LRT, lipid raft targeting; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PIP, PIP2, PIP3, phosphatidylinositol phosphates; PS, phosphatidylserine; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.