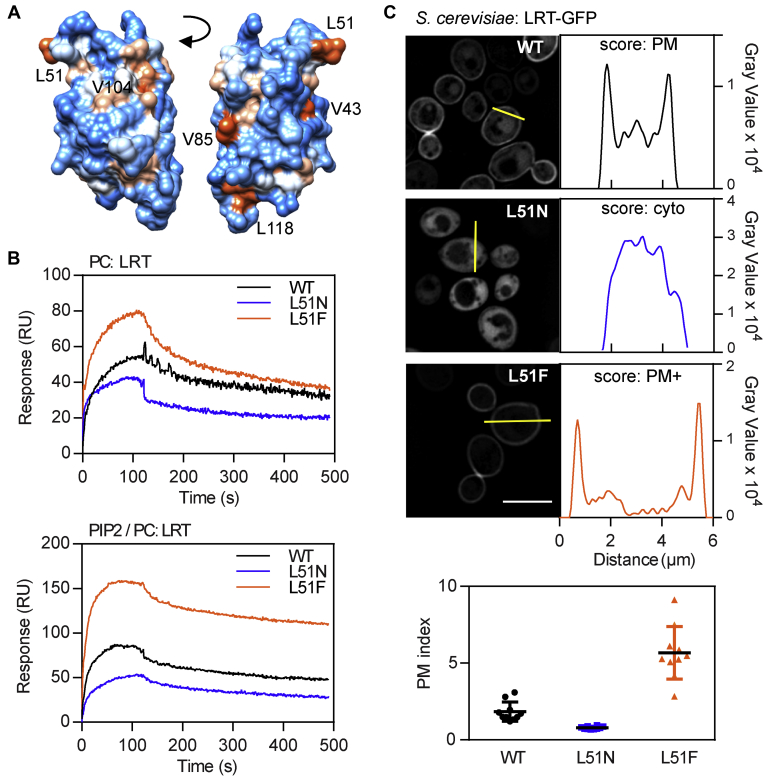
Figure 3.
Leu51 residue is involved in hydrophobic interactions of the LRT motif with a phospholipid membrane.A, surface representation of the LRT structure (aa 29–121, PDB code: 6RGN) colored according to the hydrophobicity and visualized by Chimera 1.14rc. The color gradient ranges from red for the most hydrophobic to white at 0.0 and blue for the most hydrophilic. The exposed hydrophobic residues are indicated. B, overlay plot of SPR sensograms of the interaction between LRT variants and lipid membranes. Wildtype LRT (WT), LRT-L51N, and LRT-L51F proteins at 250 nM concentration were injected over the neutravidin sensor chip coated with the immobilized lipid vesicles containing PC or PIP2/PC (5:95). The binding curves are representative of five independent “one-shot kinetic” experiments. C, localization of GFP-fused LRT variants in S. cerevisiae BY4741. Yeast cells with plasmids encoding WT or mutant L51N and L51F LRT–GFP fusion proteins were grown for 20 h in galactose-containing media to induce protein expression. Representative images from two independent experiments with the same outcome are presented. Graphs next to the fluorescence micrographs represent a fluorescence intensity profile along the yellow bar that was used for calculation of a protein plasma membrane (PM) index. See Experimental procedures for details. Values of PM indexes from ten different cells with their mean ± SD are plotted at the bottom of the image for each construct. Scale bar, 5 μm. LRT, lipid raft targeting; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.