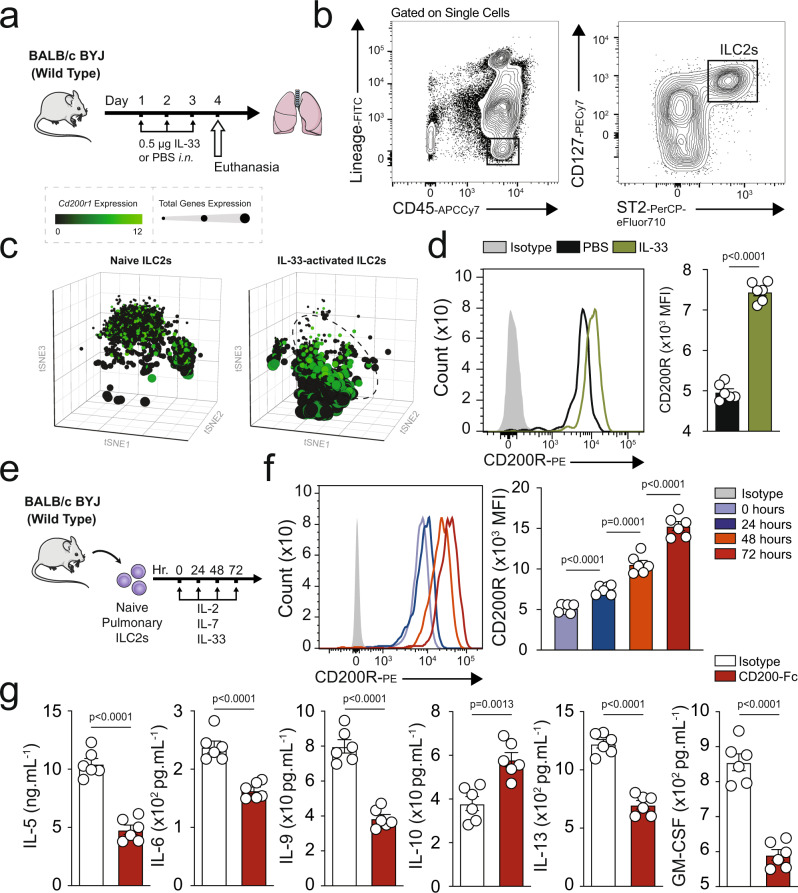
Fig. 1. Mouse ILC2s express CD200R and this expression is inducible by IL-33.
a A cohort of WT mice were challenged with recombinant mouse (rm) IL-33 (0.5 µg) or PBS intranasally (i.n.) on days 1, 2, and 3. The mice were euthanized on day 4 and the lung was isolated, as shown in the timeline. b The gating strategy of ILC2s identified as Lin−CD45+CD127+ST2+ cells. c, d mRNA (tSNE plot of 4474 naïve and 3390 activated ILC2s; dot size is indicative of the total gene expression level in each cell; dashed line encloses cells with highest CD200R expression) and protein expression levels of CD200R in both naïve and IL-33-activated ILC2s in the lungs. Corresponding quantitation of CD200R expression shown as MFI +/− SEM, n = 6 mice. e Naïve pulmonary ILC2s were sorted and subsequently cultured with rmIL-2 and rmIL-7 and rmIL-33 for 24, 48, and 72 h. f Freshly isolated ILC2s at 0 h and ex vivo activated ILC2s were analyzed by flow cytometry as indicated in the scheme and the kinetics of CD200R induction by rmIL-33 is shown. g Freshly sorted naïve and activated pulmonary ILC2s were cultured in the presence of rmIL-2 and rmIL-7 stimulated with CD200-Fc (10 µg/mL) or isotype control for 48 h. The levels of IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-13, and GM-CSF were measured by Luminex on the culture supernatants, n = 6 mice. Statistical analysis, two-tailed student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc tests; Data are shown as means ± SEMs and are representative of three individual experiments. Mouse and lung images are sourced through an open access license from Servier Medical Art.