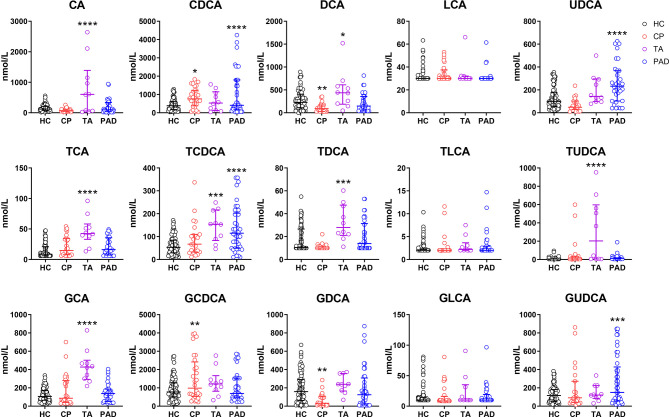
Figure 1.
Bile Acids are Altered in Chronic Periaortitis Patients. Serum was collected from healthy controls (n=88, shown in black) as well as the patients of chronic periaortitis (CP) (n=28, shown in red), Takayasu’s arteritis (TA) (n=10, shown in purple) and peripheral artery disease (PAD) (n=47, shown in blue) and tested by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Bile acid spectrum in diverse groups were then analyzed. Data are shown as median (IQR). * means patients’ data comparing to healthy controls, respectively. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. CA, cholic acid; TCA, taurocholic acid; GCA, glycocholic acid; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; TCDCA, taurochenodeoxycholic acid; GCDCA, glycochenodeoxycholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; TDCA, taurodeoxycholic acid; GDCA, glycodeoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid; TLCA, taurolithocholic acid; GLCA, glycolithocholic acid; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; TUDCA, tauroursodeoxycholic acid; GUDCA, glycoursodeoxycholic acid.