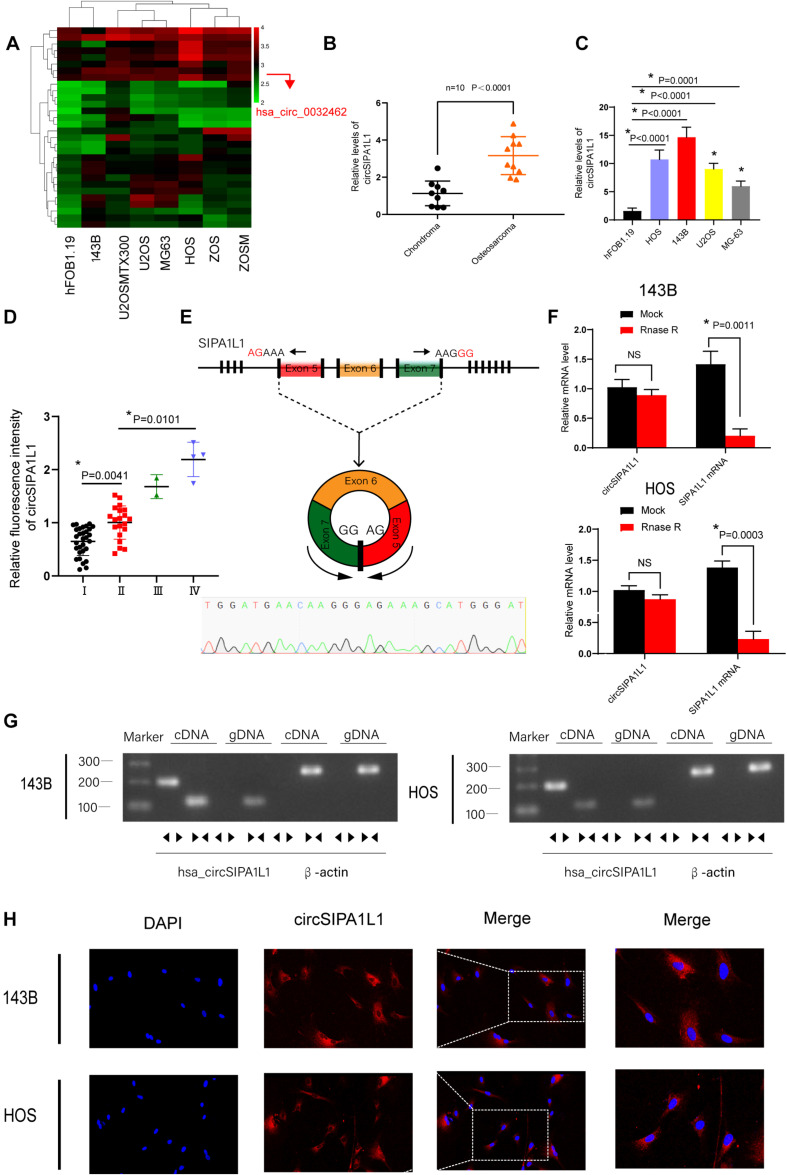
FIGURE 1.
Expression and validation of circSIPA1L1 in osteosarcoma (OS) cells and tissue. (A) Heatmap for differentially expressed circRNAs based on hFOB1.19 and OS cell lines in GSE96964. (B) circSIPA1L1 expression in 10 OS and chondroma tissue samples as detected using qRT-PCR (n = 10). (C) The expression of circSIPA1L1 was upregulated in a series of OS cell lines (HOS, 143B, U2OS, and MG-63) compared with hFOB1.19 cells. (D) The mRNA levels of circSIPA1L1 in OS at different clinical stage was detected by FISH assays on an OS tissue sample chip (56 samples in all). *P < 0.05. (E) Schematic illustration exhibited the circularization of exons 5–7 in SIPA1L1 forming circSIPA1L1 by back splicing. The existence of circSIPA1L1 was proved by Sanger sequencing. (F) The expression of circSIPA1L1 and SIPA1L1 mRNA in 143B and HOS cells was evaluated by RT-PCR, with or without RNase R treatment. (G) The existence of circSIPA1L1 was verified in 143B and HOS cells. circSIPA1L1 was amplified using divergent primers in cDNA rather than genomic DNA. GAPDH was employed as a negative control. The same or the opposite directions of the arrowhead represented divergent primers or convergent primers. (H) FISH assay showed circSIPA1L1 to mainly localize in the cytoplasm. Data from three independent experiments are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). *P < 0.05.