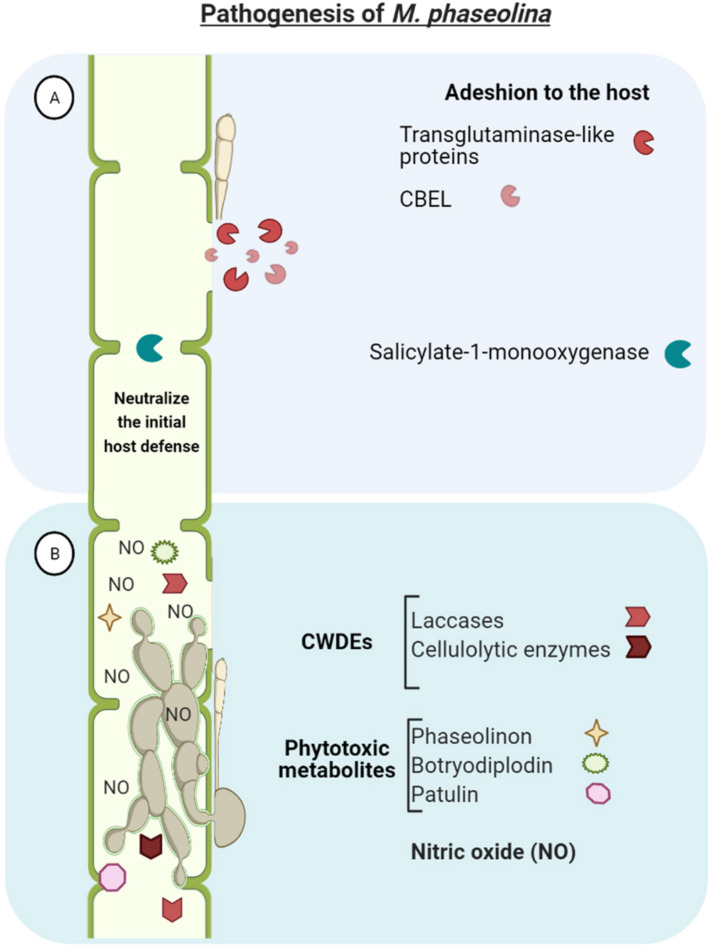
FIGURE 3.
Macrophomina phaseolina genome encodes a large repertoire of pathogenicity-associated genes which enables to (A) adhere to the host tissue (e.g., CBEL-cellulose binding elicitor lectin and transglutaminase-like proteins), neutralize the initial host defense (i.e., salicylate-1-monooxygenase), and penetrate and invade plant tissues. (B) Once in the host, the pathogen releases an array of different toxins and cell wall degrading enzymes (CDWEs) and finally disrupt the vascular system and overthrow host defense, resulting in host cell death and disease establishment.