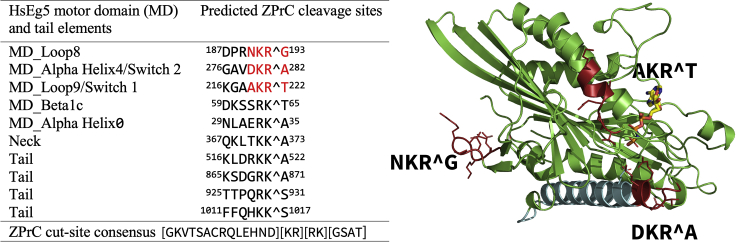
Figure 1.
List of potential ZPrC cleavage sites and corresponding secondary structure elements within HsEg5 ranked in order of decreasing likelihood of cleavage
Mass spectrometry analysis confirms in vitro cleavage by ZPrC of the sites marked in red. AMPPNP is shown in the active site in stick view, whereas the primary landmark MT-binding element of the motor domain, alpha helix4, is shown in cyan.