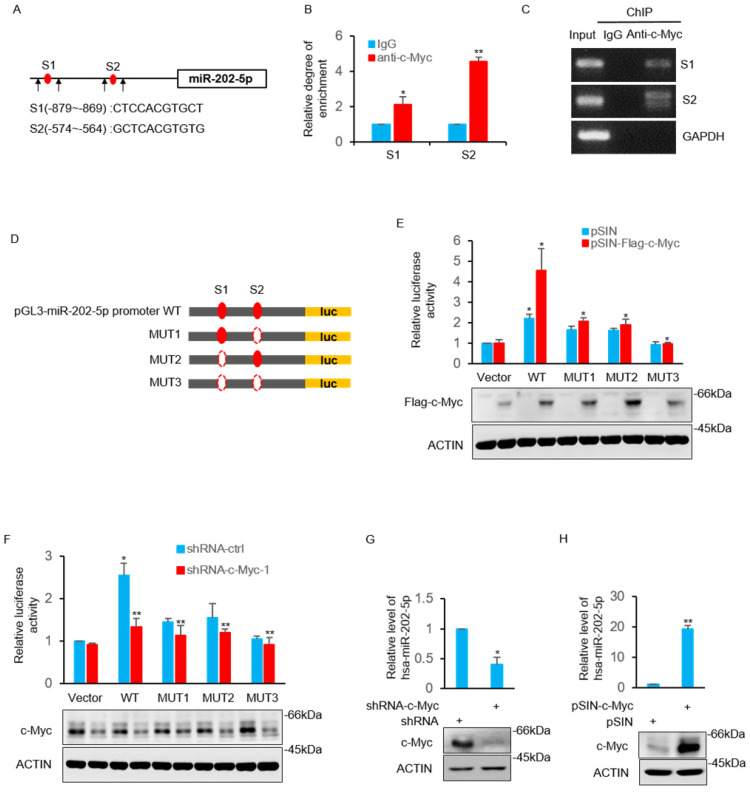
Figure 4.
MiR-202-5p is transcriptionally regulated by c-Myc. A. Schematic diagram of miR-202-5p promoter and there are two putative c-Myc binding region located in the upstream of the translational start site. Black arrows indicate primers used for PCR in (B) and (C). B-C. ChIP assays were conducted in HCT116 cells using anti-c-Myc antibodies or IgG control. ChIP products for miR-202-5p promoter along with GAPDH as a negative control was amplified by qPCR (B) or semi-quantitative RT-PCR (C). D. Schematic illustration of pGL3-basic based reporter constructs used for examining the transcriptional activity of miR-202-5p promoter response to c-Myc. Dotted lines indicated the deleted binding region. E. HCT116 cells expressing pSIN or pSIN-flag-c-Myc were co-transfected with the indicated reporter constructs and Renilla luciferase plasmids. 24 hours later, relative luciferase activity was detected by luciferase analysis and the successful expression of flag-c-Myc was examined by Western blot analysis. F. Luciferase reporter assays were conducted as per (E) to evaluate the effects of c-Myc knockdown. G. HCT116 cells were transduced with the shRNA-ctrl or shRNA-c-Myc and miR-202-5p expression was examined using qPCR. H. HCT116 cells were transduced with pSIN or pSIN-c-Myc and miR-202-5p expression was evaluated using qPCR. All data are representative of three independent experiments.