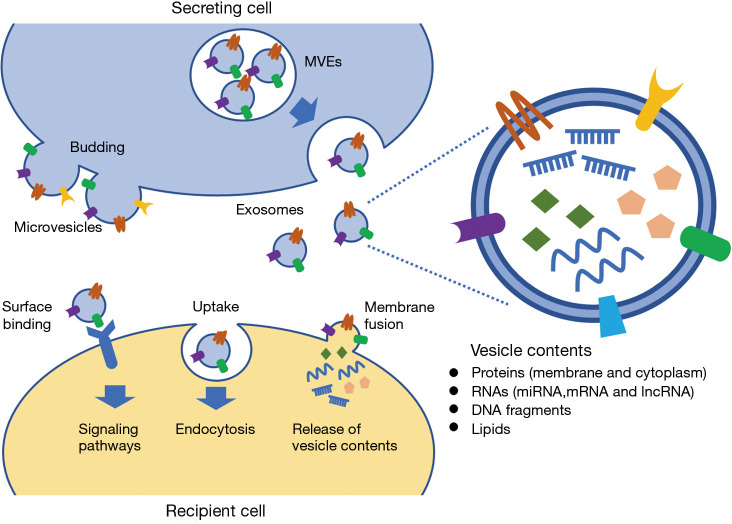
Figure 1.
Biogenesis and biological function of EVs. Microvesicles are formed by budding of the plasma membrane. Exosomes are formed as intraluminal vesicles within the lumen of multivesicular endosomes (MVEs), and then, released by the fusion of MVEs with the plasma membrane. EVs are enclosed by a lipid bilayer, containing various molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids and lipids. EVs are the mediators of intercellular communication, via the transfer of vesicle contents from the secreting cells to the recipient cells by uptake and membrane fusion. EVs also initiate intracellular signaling pathways via surface binding.