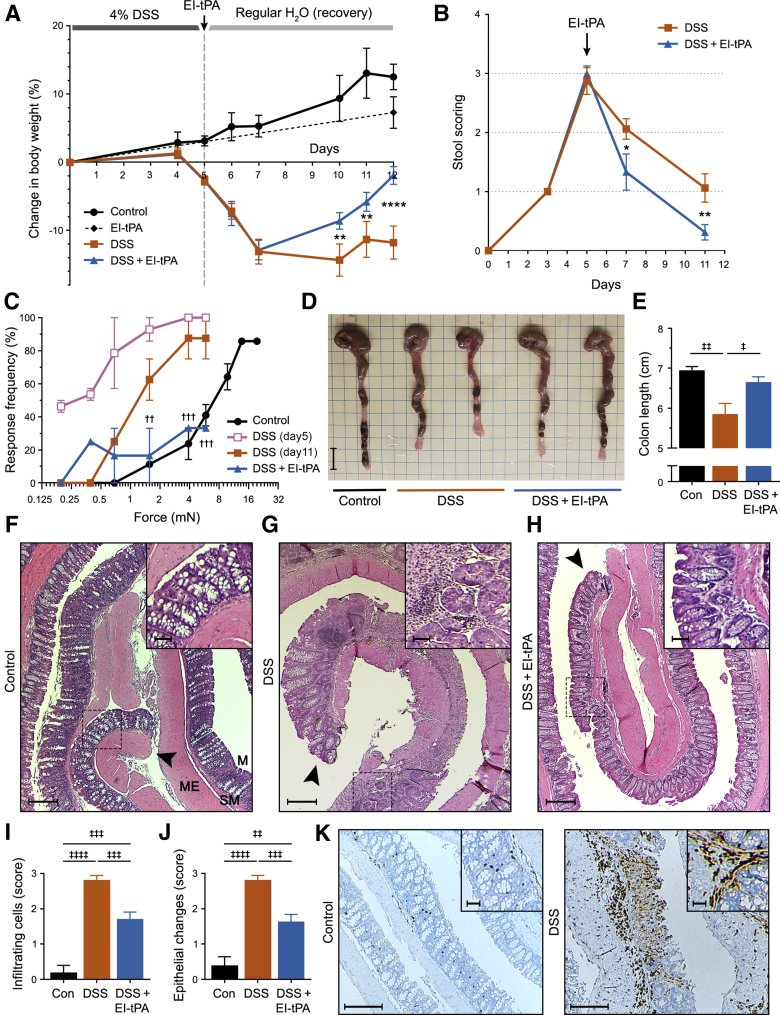
Figure 1.
Enzymatically inactive tissue-type plasminogen activator (EI-tPA) reverses colitis in mice treated with 4% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) for 5 days. A: Mice were exposed to 4% DSS in the drinking water for 5 days and then injected with EI-tPA (blue curve) or vehicle (orange curve) intravenously. Control (Con) mice were not exposed to DSS (black curve). Mice that were not exposed to DSS but injected intravenously with EI-tPA are shown with a dashed black line. Weight is expressed relative to that recorded on day 0. B: Mice were exposed to 4% DSS for 5 days and then treated with EI-tPA or vehicle. Stool scores were determined on the indicated days. C: Mice were probed in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen with von Frey filaments to detect sensitivity. Increased response rate to specific filaments reflects increased sensitivity. Cohorts of nine mice were studied, including control mice not exposed to DSS (black circles), mice exposed to 4% DSS for 5 days and tested on day 5 (pink open squares), mice exposed to DSS and tested on day 11 (orange closed squares), and mice exposed to DSS, treated with EI-tPA on day 5, and tested on day 11 (blue triangles). D: Representative images of colons harvested from mice that were not DSS exposed (Control), mice exposed to DSS for 5 days and then allowed to recover for 7 days (DSS), and mice exposed to DSS for 5 days, treated with EI-tPA on day 5, and then allowed to recover for 7 days (DSS + EI-tPA). E: Colon length results are summarized. F–H: Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained sections of colons harvested from mice not exposed to DSS (Control; F), mice exposed to 4% DSS for 5 days and then allowed to recover for 7 days (DSS; G), and DSS-exposed mice treated once with EI-tPA on day 5 and then allowed to recover for 7 days (DSS + EI-tPA; H). F: The control colon is marked to show the mucosa (M), which includes epithelium-lined crypts adjacent to the colon lumen, the submucosa (SM), and the muscularis externa (ME). The arrowheads indicate the distal ends of the colon sections. Boxed areas are shown at higher magnification in the insets. I and J: H&E sections of colons recovered from mice that were not DSS-exposed (Con), exposed to DSS (DSS), and exposed to DSS with subsequent EI-tPA treatment (DSS + EI-tPA) were scored for infiltration of inflammatory cells and epithelial changes in the distal 25% segment. K: Sections of colons from mice that were not DSS-exposed (Control) and exposed for 5 days to 4% DSS were immunostained to detect CD11b. High magnification areas are shown in the insets. Data are presented as as means ± SEM (E, I, and J). n = 9 mice exposed to 4% DSS in the drinking water for 5 days and then injected with EI-tPA or vehicle (A); n = 7 control mice not exposed to DSS (A); n = 4 mice not exposed to DSS but injected intravenously with EI-tPA (A); n = 7 (E); n = 11 to 14 (I and J). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 DSS versus DSS + EI-tPA; ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001 DSS (day 11) versus DSS + EI-tPA; ‡P < 0.05, ‡‡P < 0.01, ‡‡‡P < 0.001, and ‡‡‡‡P < 0.0001. Scale bars: 1 cm (D); 10 μm (F–H and K, main images); 2 μm (F–H and K, insets).