Fig 5.
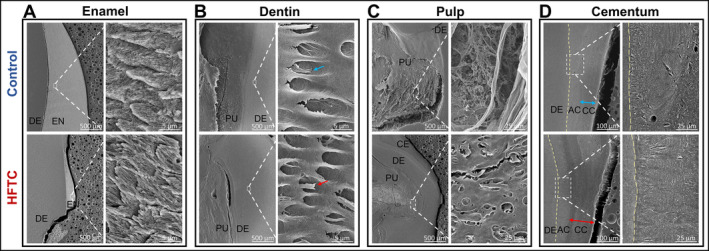
Scanning electron micrographs (SEMs) of control and teeth of a patient with hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC; patient 15). For each set of panels, low magnification views are on the left and high magnification views are on the right. (A) Organized enamel rods are observed in both control and HFTC teeth. (B) Normal dentinal tubules and odontoblast processes are observed in control (blue arrow) and HFTC (red arrow) teeth. (C) Pulpal cell‐like and fiber‐like structures are observed in control, whereas disorganized dentinal tubules are observed in HFTC pulp. (D) Organized acellular and cellular cementum are observed in control teeth. Cellular cementum in HFTC tooth appears to be thicker compared with control. The junction between dentin and acellular cementum is harder to differentiate in the HFTC tooth. Additional SEM images of the pulp are provided in Supplementary Information Figure S4. AC, Acellular cementum; CC, cellular cementum; CE, cementum; DE, dentin; PU, pulp.
