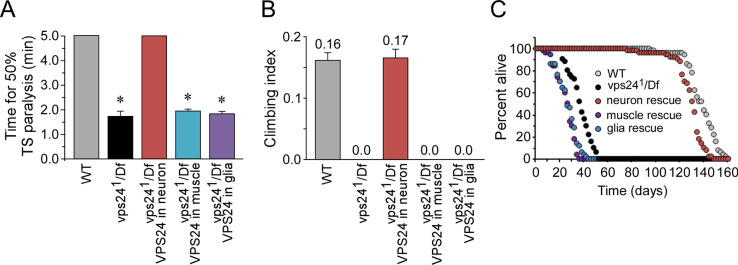
Fig 2. Neuronal expression of the wild-type VPS24 protein rescues the vps241 TS paralytic phenotype as well as locomotor and lifespan deficits.
(A) The TS paralytic phenotype of the vps24 mutant was rescued by expression of the wild-type EGFP-VPS24 in neurons but not in muscle or glia. The GAL4 drivers for neuronal, muscle and glial expression were Appl-GAL4, Mhc-GAL4 and Repo-Gal4 respectively. (B) Climbing tests, carried out at a room temperature (RT) of 22–24°C, indicated no detectable climbing ability in the vps24 mutant. The climbing tests were truncated at 2 min if 50% climbing had not occurred and zero was given for the climbing index. (C) Loss of the VPS24 function reduced lifespan with respect to WT when raised at a permissive temperature of 20°C. These mutant phenotypes were rescued by expression of wild-type EGFP-VPS24 in neurons but not in muscle or glia. The same GAL4 drivers were used for subsequent cell-type specific expression studies.