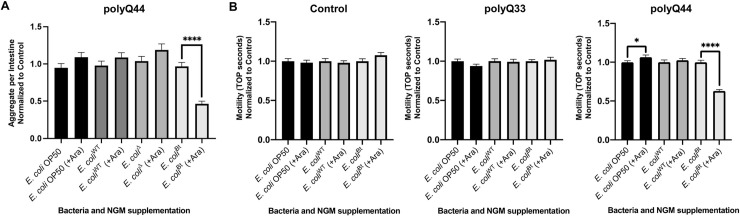
Fig 8. Butyrate-producing E. coli suppresses aggregation and the associated toxicity.
Animals were fed four different strains of bacteria: non-butyrogenic controls (E. coli OP50, E. coliWT, E. coliΔ) and conditional butyrogenic E. coli (E. coliBt). A) The graphs represent the average number of intestinal polyQ44 aggregates per worm normalized to the control (no arabinose). Each bar is an average of three independent experiments with a total of 100 animals. B) Intestinal aggregate-dependent toxicity normalized to the control (no arabinose) assessed with the TOP phenotype. The left panel represents roller worms (Control), the middle panel represents polyQ33 worms, and the right panel represents worms expressing polyQ44. Each bar is an average of three independent experiments with a total of 60 animals. Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance between each pair was calculated using Student’s t-test (*p<0.05, ****p<0.0001).