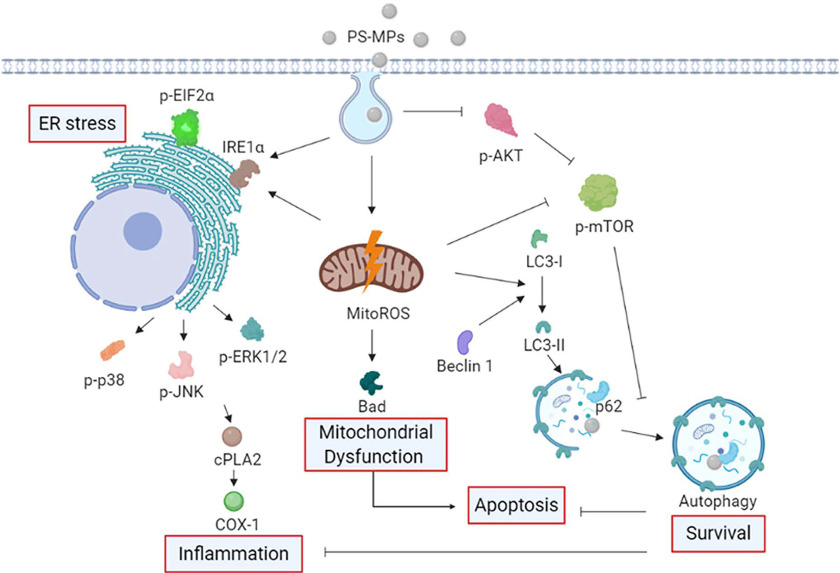
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram indicating the proposed mechanism by which PS-MPs induced mitochondrial ROS production, Bad expression, ER stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Based on the data obtained in HK-2 cells and a mouse model, we propose that PS-MPs were taken up by kidney cells and that PS-MPs induced mitochondrial ROS production and Bad protein expression. Furthermore, we propose that PS-MPs increased the expression of the ER stress-related proteins and and the inflammation-related proteins and COX-1 in kidney cells. We propose that PS-MPs increased the autophagy-related protein expression of Beclin 1, and LC3 in kidney cells and affected ER stress, inflammation, and autophagy in the kidney cells via MAPK and AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Mitochondrial ROS-mediated regulation of Bad, , and LC3 in kidney cells can occur via AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Furthermore, autophagy may be an adaptive stress response that inhibits inflammation and apoptosis. Note: AKT, protein kinase B; COX-1, cyclooxygenase-1; , cytoplasmic phospholipase A2; , eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HK-2 cells, human kidney 2 cells; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mitoROS, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species; mTOR, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PS-MPs, polystyrene microplastics; ROS, reactive oxygen species.