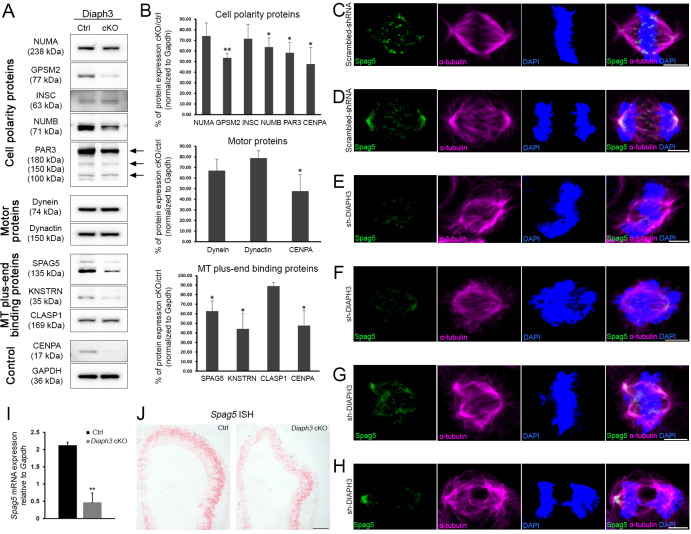
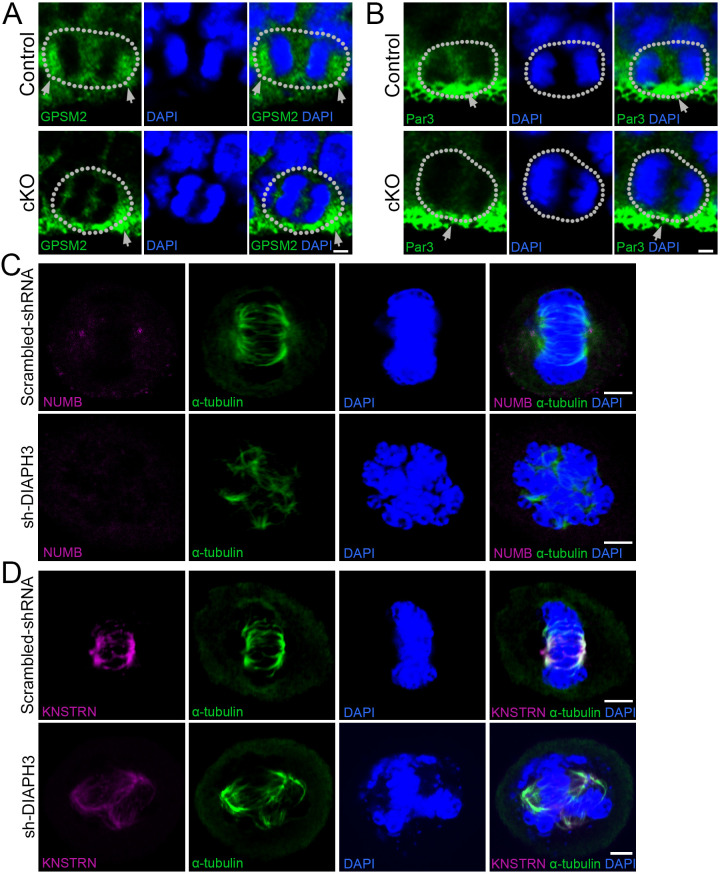
Figure 2. Diaph3 deficiency impairs the expression and stability of mitotic spindle polarity proteins.
(A, B) Assessment of nuclear mitotic apparatus (NUMA), G-protein signaling modulator 2 (GPSM2), INSC, NUMB, PAR3, Dynein, Dynactin, SPAG5, KNSTRN, and CLASP1 levels in telencephalon extracts of Diaph3 cKO embryos by western blotting. CENPA was used as positive control (Liu and Mao, 2016) and GAPDH as loading control for quantification. Both the higher and lower bands of SPAG5 were quantified. n = 4 embryos for each genotype. *p<0.05, ** p<0.01, Student’s t-test; error bars represent s.e.m. Fold change and p-value are listed in Supplementary file 2. (C–H) Representative images of mitotic cells transfected with scrambled shRNA (C, D) or DIAPH3 shRNA (sh-DIAPH3, E–H), and immunostained with anti-SPAG5 (green) and anti-α tubulin (magenta) antibodies. Chromosomes were counterstained with DAPI (blue). SPAG5 localized at the centrosome and kinetochore in control cells (C, D), and both its expression level and distribution were altered in DIAPH3 knockdown cells (E–H). Scale bar, 5 μm. n = 118 and 115 cells from five individual experiments of scrambled shRNA and sh-DIAPH3, respectively. (I) Quantification of the Spag5 mRNA by real-time RT-PCR. There is a reduction of 78% in Diaph3 cKO relative to control mice (p=0.0046). n = 3 from nine embryos for each genotype. (J) Coronal sections of e11.5 forebrain from control (left) and Diaph3 cKO (right, hybridized with a Spag5 fast red-labelled RNAscope probe). The expression of Spag5 mRNA is downregulated in Diaph3 cKO; scale bar, 150 µm. n = 3 for each genotype.