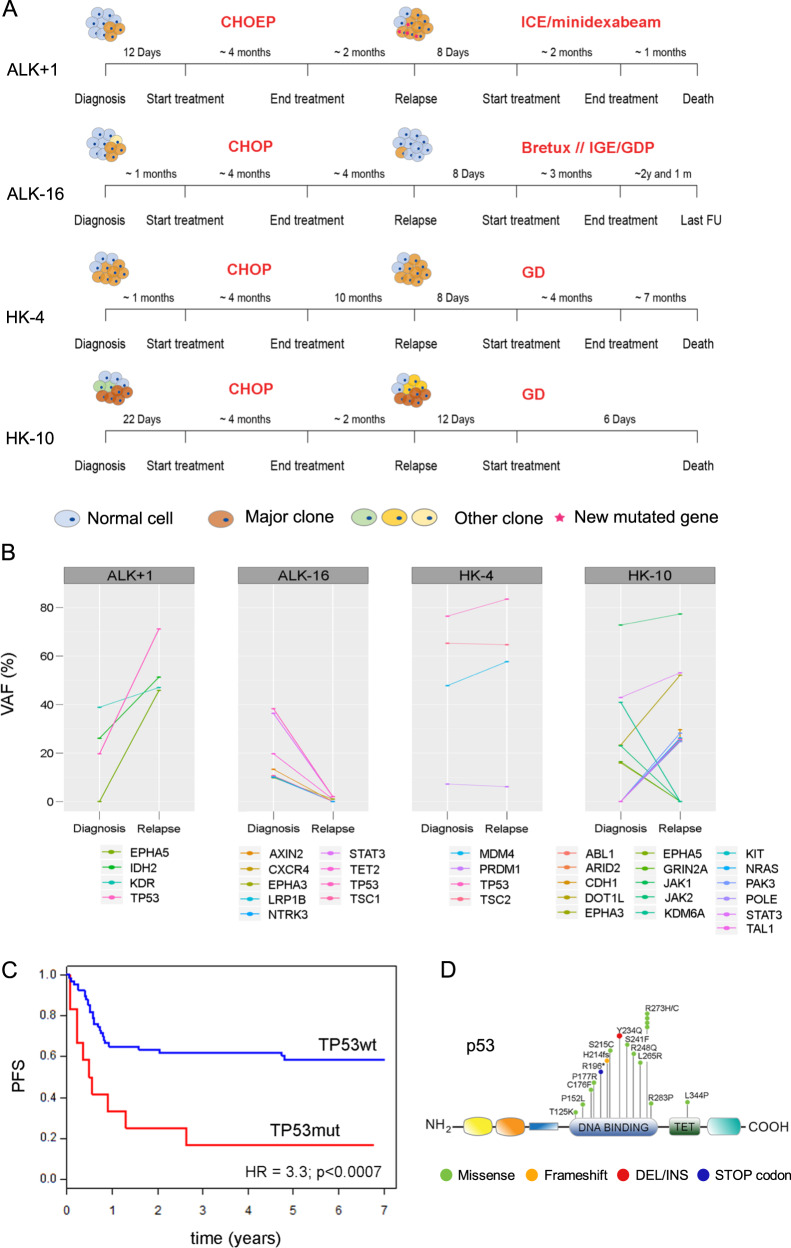
Fig. 2. Diagnosis versus relapse showed mutatedTP53to be associated with a shorter PFS in sALCL.
a Schematic representation of four patients sequenced at diagnosis and at relapse highlighting their clinical path and treatment. Meaning of the color is described in the legend. CHOEP chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, etoposide, vincristine and prednisone, CHOP chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone, ICE chemotherapy combination that includes ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide, bretux: brentuximab vedotin, GDP gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin, GD gemcitabine and docetaxel, FU follow up. b Changes in mutational burden during tumor progression. The percentage of variant allele frequency (VAF%) for each gene is plotted at diagnosis and at relapse. The names of genes involved are reported under each plot. c 7-year PFS in systemic ALCL patients according to TP53 status; red: TP53 mutated (mut) patients; blue: TP53 wild-type (wt) patients. P values and hazard ratios (HR) shown were determined by Cox proportional hazards. d Schematic representation of p53 domains and the variants detected.