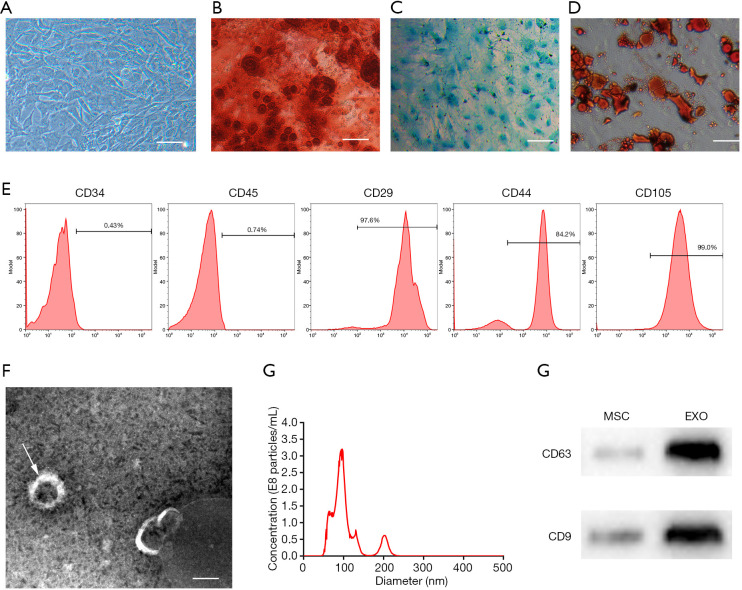
Figure 1.
Characterization of hAFMSCExos. (A) The morphology of hAFMSCs under a light microscope; scale bar: 300 µm. (B,C,D) The multipotent nature of hAFMSCs was confirmed by adipocyte, osteoblast, or chondroblast differentiation after corresponding differentiation media culture, and Alizarin Red staining (B), Alcian Blue staining (C), and Oil Red O staining (D) were tested respectively; scale bar: 100 µm. (E) Characterize the phenotype of hAFMSCs by flow cytometric analysis. (F) The morphology of hAFMSCExos under electron microscopy; the arrow indicated the hAFMSCExos; scale bar: 100 nm. (G) The particle size distribution of the hAFMSCExos by nanoparticle tracking analysis. (H) Traditional exosomal markers, CD9 and CD63 were tested by Western blot in the hAFMSCExos. hAFMSCExos, human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; hAFMSCs, human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells.