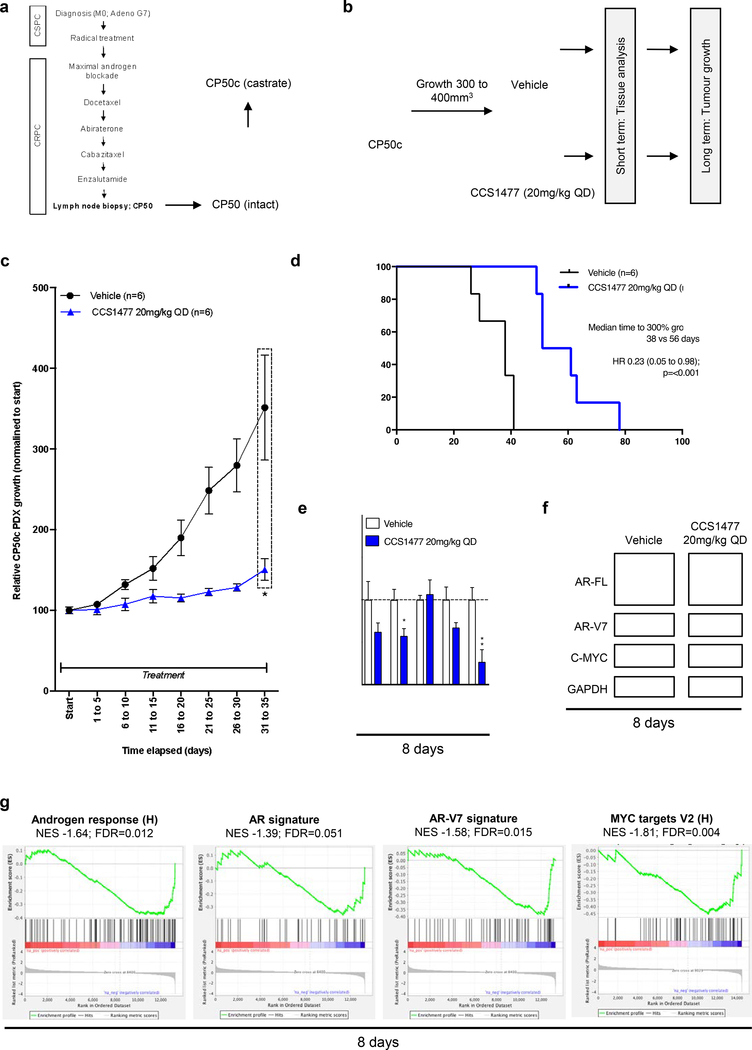
Figure 6: CCS1477 decreases AR and AR-V7 signaling and inhibits growth in a patient- derived model of lethal prostate cancer.
(a) Patient-derived xenograft (PDX) CP50c was developed from lymph node biopsy from a patient who had progressed through all standard-of-care treatments for CRPC. (b) Schematic overview of CP50c PDX experimental design. Once CP50c PDX tumor volume reached 300mm3 treatment, administered by oral gavage, commenced with either vehicle or 20 mg/kg CCS1477 daily (QD) until reaching 300% of starting volume (long term, n=6 per group), with an additional subset treated for short term analysis at 8 days (n=4 per group for mRNA; n=3 for western blot). (c-d) Mean growth (normalized to start; defined as 100%) with standard error of mean was determined for each tumor. p-value (*p=<0.05, **p=<0.01, ***p=<0.001) was calculated for vehicle compared to CCS1477 at 20 mg/kg QD at 31 to 35 days using unpaired student t-test. (c). Time to reach 300% growth was used as a surrogate endpoint for survival. Hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals and p-values for univariate cox survival model are shown (d). (e-f) The effect of 20mg/kg CCS1477 QD compared to vehicle at eight-days on AR, AR-V7, KLK3, TMPRSS2, and C-MYC mRNA expression (e) and on AR- FL, AR-V7, C-MYC, and GAPDH protein expression was determined (f). Mean mRNA expression (normalized to an average of B2M/GAPDH/HPRT1 and vehicle treatment; defined as 1.0) with standard error of mean from individual tumors in each group is shown. p-values (*p=<0.05, **p=<0.01, ***p=<0.001) were calculated for each treatment condition compared to vehicle using unpaired student t-test. (g) Gene set enrichment analysis of RNA-sequencing from vehicle group and 20mg/kg CCS1477 QD group at 8-days comparing the androgen response (left), AR signature (center left), AR-V7 signature (center right) and MYC targets V2 (right) with normalized enrichment score (NES) and false discovery rate (FDR) presented.