Figure 7.
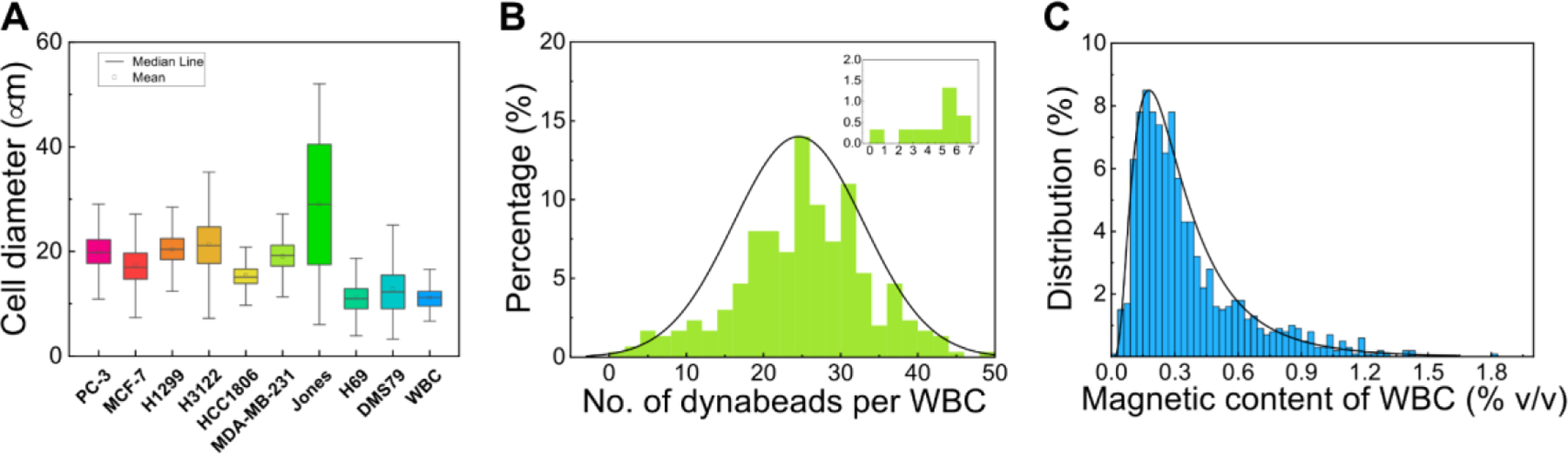
Measurement of physical size distribution of cancer cells and magnetic labeling of WBCs. (A) Size distribution of cancer cell lines – Prostate cancer (PC-3), Breast cancer (MCF7, MDA-MB-231, HCC1806), non-small cell lung cancer (H1299, H3122), small cell lung cancer (DMS79, H69), and white blood cells from healthy donors. (B) Percentage of labeled WBCs versus the number of magnetic beads (dynabeads) per WBC (n=500). The average dynabeads per WBC was 25 ± 8 (mean ± standard deviation). The insert was the percentage of WBCs labeled with <= 7 dynabeads. More than 99.5% of WBCs were labeled with more than one dynabeads (C) Percentage of labeled WBCs versus their volumetric fraction of magnetic materials. The volume fraction of magnetic materials in a WBC ( was calculated based on the following parameters – number of Dynabeads on each WBC (n), the diameter of the WBC in question (), the volume fraction of magnetic materials in each Dynabead (), and the diameter of the Dynabead (). The volume fraction of magnetic materials in each Dynabead () was provided by the manufacturer to be 11.5% (v/v), and the diameter of the Dynabead () is 1.05 μm. The number of Dynabeads on each WBC (n) was determined experimentally from image analysis, and the diameter of the WBC in question () was calculated using their surface areas with the assumption that cells were spherical.
