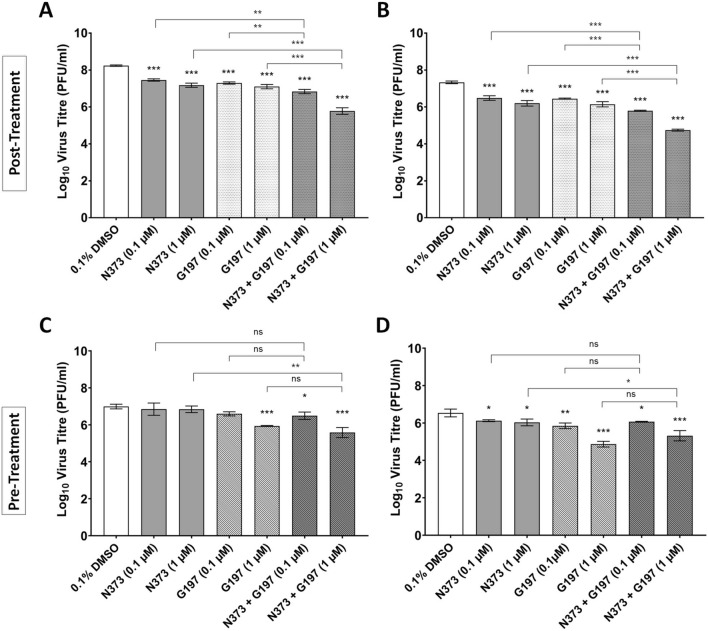
Figure 4.
Treatment with both N373 and G197 exhibited greater inhibition of EV-A71 replication compared to single compounds when cells were treated after virus inoculation and not before. RD cells treated with N373 and G197 at the indicated combinations and concentrations were infected with EV-A71 after compound removal. Combination treatment (N373 + G197) at both concentrations resulted in virus titres lower than either of the single compound treatments at both MOI = 1 (A) and MOI = 0.1 (B). (C) RD cells were pre-treated for 2 h with N373 and G197 at the indicated combinations and concentrations prior to infection at MOI = 1 and (D) MOI = 0.1. Combination treatment did not result in a significantly lower virus titre compared to treatment with G197 only and N373 slightly reduced virus titres at a lower MOI. Statistical analysis for differences in virus titre due to drug treatment was performed with one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test: *(p < 0.05), **(p < 0.01), ***(p < 0.005). Student’s t-test was performed to compare single compound treatments (G197 or N373) to combination treatment at the same concentration.