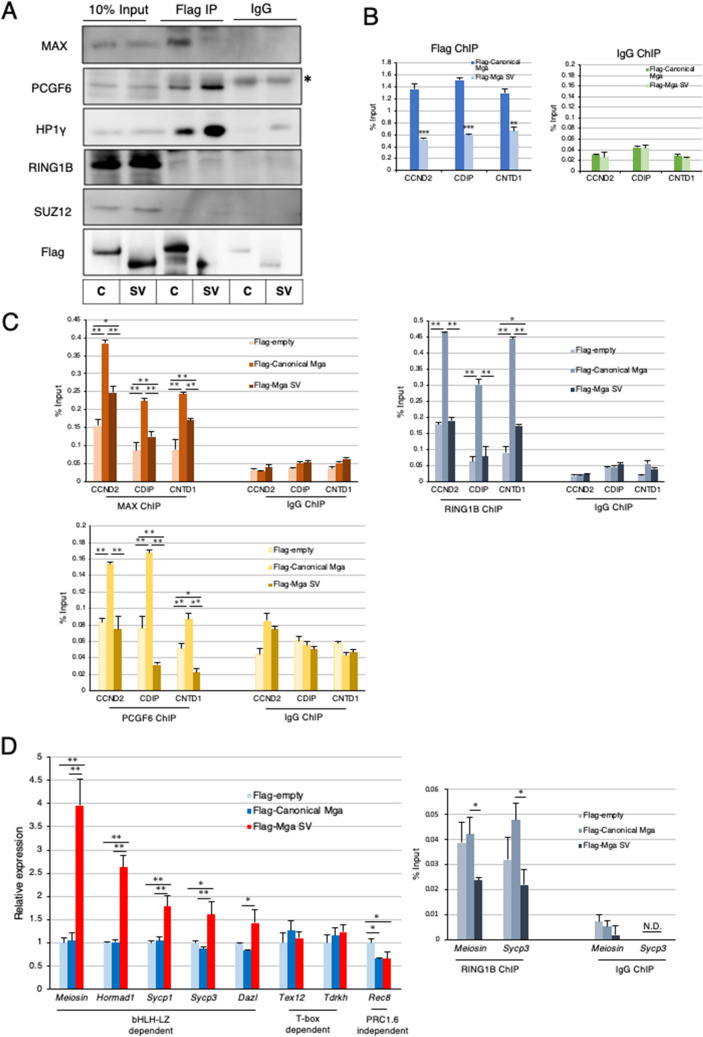
Figure 5.
Dominant negative effect of carboxy-terminally truncated MGA on PRC1.6. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation analyses of canonical and carboxy-terminally truncated MGAs. Expression vectors for Flag-tagged canonical and carboxy-terminally truncated MGAs were transiently introduced individually into MGA-null HEK293FT cells by transfection. Coimmunoprecipatations were performed with an anti-Flag-tag antibody using nuclear extracts from the transfected cells. Coimmunoprecipitated proteins were used to examine the presence or absence of SUZ12 as well as PRC1.6 components (PCGF6, L3MBTL2, HP1γ, and RING1B). C and SV stand for canonical- and splice variant, respectively. *Indicates signals of the immunoglobulin heavy chain used for immunoprecipitation. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S7. (B) ChIP-qPCR analyses of PRC1.6-target genes in MGA-null HEK293FT cells producing Flag-tagged canonical or carboxy-terminally truncated MGA transiently with the anti-Flag-tag antibody. Control IgG was used as a negative control. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. The Student’s t-test was conducted to examine statistical significance. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) ChIP-qPCR analyses of PRC1.6-target genes in MGA-null HEK293FT cells with empty vector and those producing either Flag-tagged canonical or carboxy-terminally truncated MGA transiently with antibodies against MAX, RING1B or PCGF6. Control IgG was used as a negative control. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. The Tukey–Kramer test was conducted to examine statistical significance. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (D) Effects of forced expression of Mga SV on meiosis-related genes in mouse ESCs Expression vectors to produce Flag-tagged canonical and carboxy-terminally truncated MGAs and that with no cDNA (empty) were transiently introduced individually into mouse ESCs by transfection. Transfected cells were collected as GFP-positive cells. Then, RNAs prepared from them were used to quantify expression levels of meiosis-related genes (left panel). The same sets of ESCs were also used for ChIP-qPCR analyses of Meiosin and Sycp3 promoter loci with antibody against RING1B (right panel). Control IgG was used as a negative control. N.D. not detected. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Data were subjected to statistical significance examination as in C. *P < 0.05.