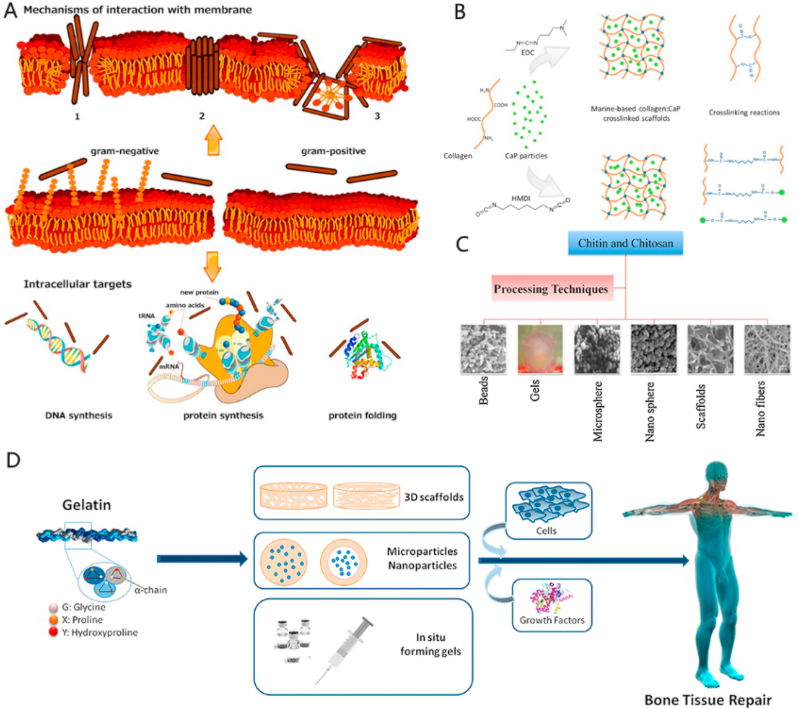
Fig. 7.
(A) Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) kill bacteria by inducing membrane damage and/or internalization. An alternative antibacterial mechanism of AMPs is intracellular targeting. Some AMPs act on intracellular targets by inhibiting cell wall synthesis, nucleic acid binding and synthesis, protein production and enzyme activity. (B) Schematic of crosslinking reactions between 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) crosslinking agents. (C) Various forms in which chitin and chitosan constructs can be fabricated. (D) Gelatin used for bone tissue repair. (A is reproduced from Ref. [298] with permission from publisher; B is reproduced from Ref. [299] with permission from publisher; C is reproduced from Ref. [300] with permission from publisher; D is reproduced from Ref. [301] with permission from publisher).