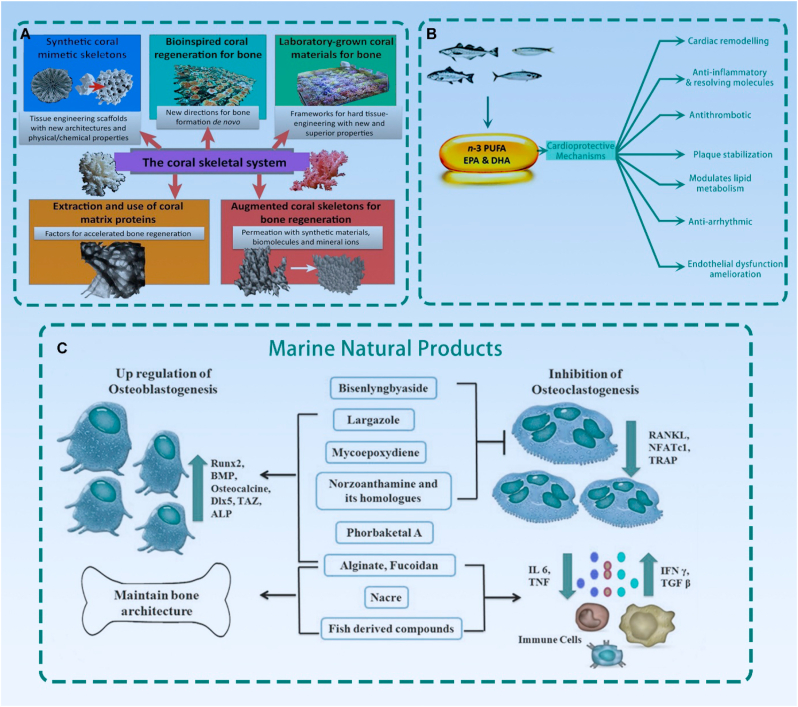
Fig. 9.
A) New biomedical uses of coral skeletons. B) Purported cardioprotective mechanisms associated with fish and fish oil-derived n-3 PUFAs. C) Effect of marine-derived materials on bone metabolism via up-regulation of osteoblastogenesis and downregulation of osteoclastogenesis. Some are directly involved in osteoblastogenesis by increasing the expression of Runx2, BMP and other transcription factors. Others are dependent on the regulation of cytokine production (IL-6 and TNF). Marine-derived compounds suppress osteoclastogenesis through downregulating the expression of RANKL, NFATc1 and TRAP) (A is reproduced from Ref. [329] with permission from the publisher; B is reproduced from Ref. [330] with permission from the publisher; C is reproduced from Ref. [331] with permission from the publisher).