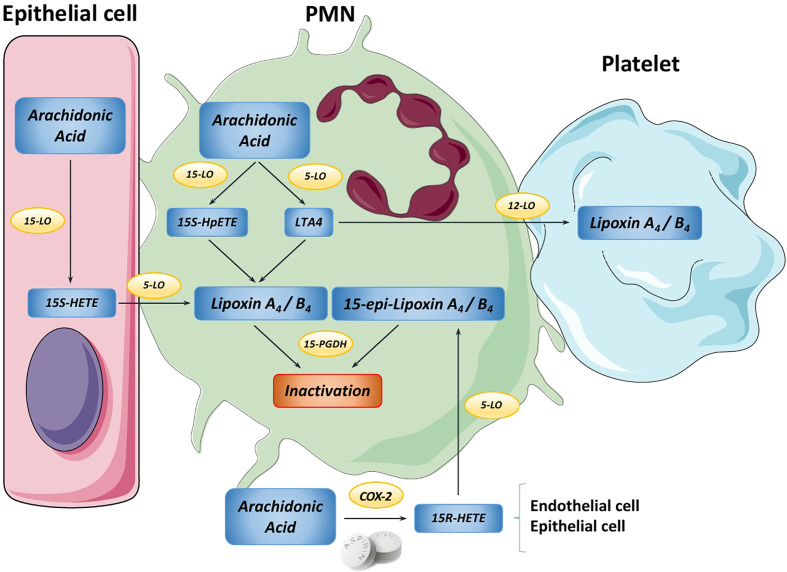
Figure 2.
Overview of the main lipoxin biosynthetic pathways. In the PMN cell, Arachidonic Acid (AA) can be converted into either 15S-HpETE or Leukotriene A4 (LTA4) by 15-LO and 5-LO, respectively. Then, these metabolites are transformed into native lipoxin A4 or B4. Moreover, platelets can use LTA4 from PMNs to produce LXA4/B4 in a process known as transcellular biosynthesis. Likewise, in epithelial cells AA is transformed by 15-LO into 15-HETE, which is transferred to PMNs to produce LXA4/B4. Endothelial cells can use AA to yield the intermediate 15R-HETE by COX-2, step that is promoted by aspirin. This transitional molecule is metabolized by PMNs to generate the “aspirin-triggered” 15-epi-lipoxins A4 and B4. Finally, both native and aspirin-triggered LXs can be rapidly inactivated by 15-PGDH, stopping the downstream signaling.