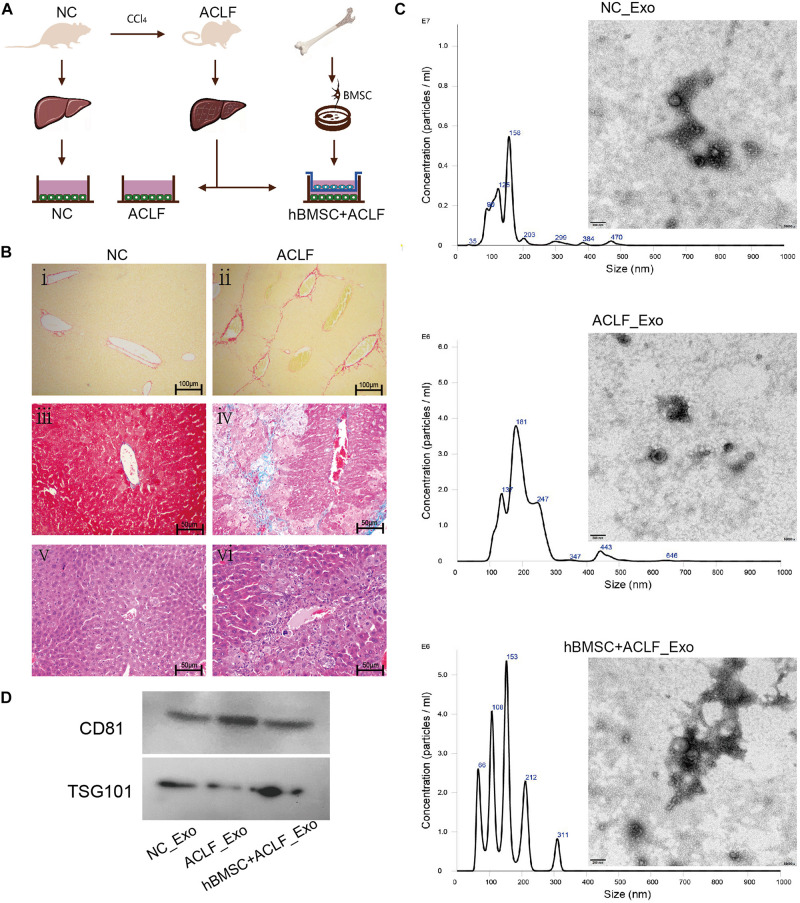
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of the ACLF model and the derived exosomes. (A) ACLF was induced in mice using carbon tetrachloride, and then primary hepatocytes were isolated and cultured in vitro, in the absence or presence of MSCs. Cells from healthy animals were collected as controls. The supernatants of the three groups of cells were then collected for exosome extraction. (B) Sirius red staining (i-ii, scale bar = 100 μm), Masson’s trichrome staining (iii–iv, scale bar = 50 μm) and H&E staining (v–vi, scale bar = 50 μm) reveal significant fibrosis, collagen deposition, and inflammatory cell infiltration and necrosis, respectively, in the livers of ACLF mice. (C) NTA and TEM-based analyses of exosomes reveal that the particles are concentrated in the 200-nm range and have a cup-like bilayer structure. (D) Western blotting reveals the expression of the exosome membrane marker CD81 and of the intra-particle marker TSG101.