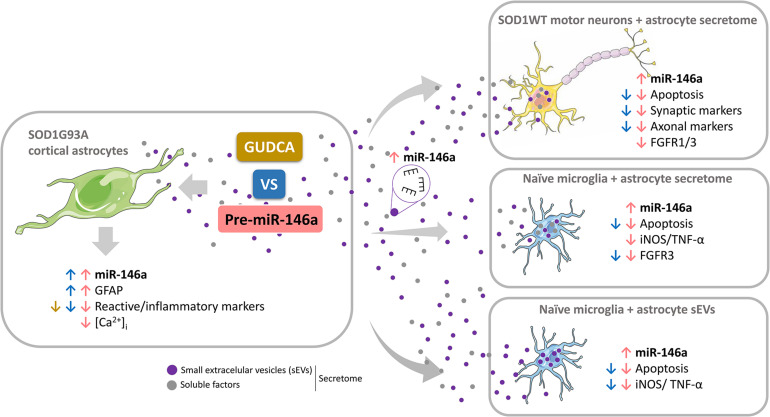
FIGURE 10.
Schematic representation of the efficacy of miR-146a replenishing methods to recover the neuroprotective phenotype of aberrant mSOD1 cortical astrocytes, and in preventing toxic paracrine signaling toward motor neurons and microglia by the mediators released from the pathological astrocytes. Astrocytes were isolated from the cortex of SOD1-G93A (mSOD1) mice pups at 7-day-old and cultured for 13 days in vitro, showing an aberrant/reactive phenotype. Treatment with glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA) and dipeptidyl vinyl sulfone (VS) abrogated reactive markers, with additional re-establishment of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and miR-146a by VS, evidencing their reparative ability. Transfection of mSOD1 astrocytes with pre-miR-146a also attenuated their phenotypic aberrancies and intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) overload. Moreover, such treatment increased miR146a content in the cell-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), and mediated miR-146a enrichment in SOD1-WT motor neurons (MNs) and naïve N9 microglial cell. Secretome from mSOD1 astrocytes increased early/late apoptosis and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) gene levels in MNs and microglia, effects that were prevented by pre-miR-146a or VS modulation. These strategies led to a secretome with preventable properties over the deregulation of synaptic dynamics and axonal transport upon the pathological extracellular milieu from mSOD1 astrocytes. The pre-miR-146a-treated cells also prevented microglia activation through their secretome or isolated sEVs, but in the case of VS only the isolated sEVs showed such property. Data reveal that both pre-miR-146a and VS-mediated miR-146a replenishment in mSOD1 cortical astrocytes are promising approaches to recover the neuroprotective phenotype of ALS cortical astrocytes and the microglia and MN homeostatic balance in the disease. [Ca2+]i, intracellular calcium; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; GUDCA, glycoursodeoxycholic acid; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; miR-146a, miRNA-146a; SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis alpha; VS, dipeptidyl vinyl sulfone.