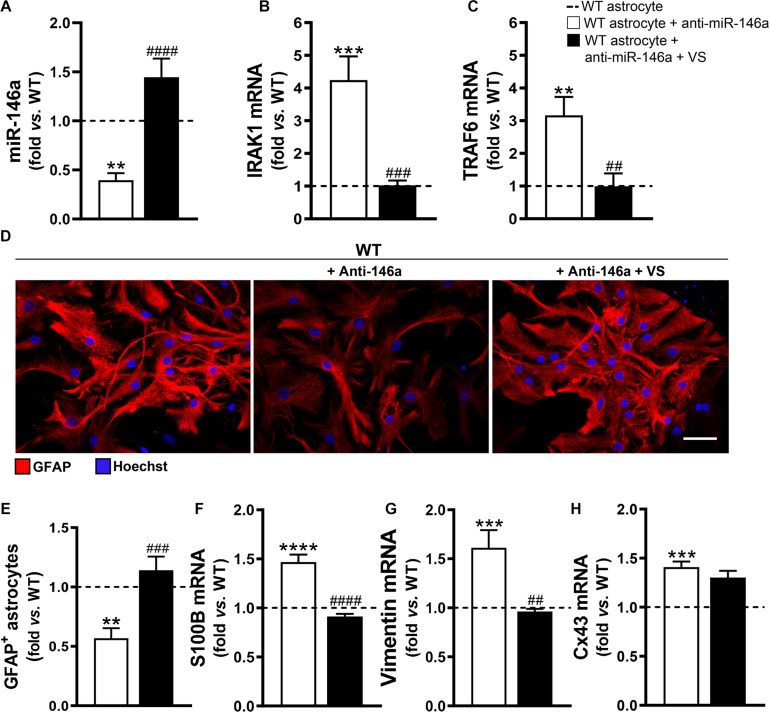
FIGURE 3.
VS rescues GFAP levels and abolishes vimentin- and S100B-associated reactivity induced by the miR-146a inhibitor in WT astrocytes. Astrocytes were isolated from the cortex of wild type (WT) mice with 7-day-old and cultured for 13 days in vitro. Transfection with anti-miR-146a followed by treatment with dipeptidyl vinyl sulfone (VS) was performed in these cells. RT-qPCR analysis of (A) miRNA(miR)-146a, (B) interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase-1 (IRAK1), (C) TNF receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6), (F) S100 calcium-binding protein B (S100B), (G) vimentin and (H) connexin-43 (Cx43) was performed. SNORD110 was used as reference gene for (A) analysis and β-actin for (B,C,F–H) analysis. (D) Representative images of astrocytes stained with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, red) in red by immunocytochemistry and (E) respective quantification of the GFAP-positive cells. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye (blue). Results are mean (±SEM) fold change vs. untreated WT astrocytes from at least three independent experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. untreated WT astrocytes; ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, and ####p < 0.0001 vs. WT astrocytes treated with anti-miR-146a. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test was used. Scale bar represents 20 μm.