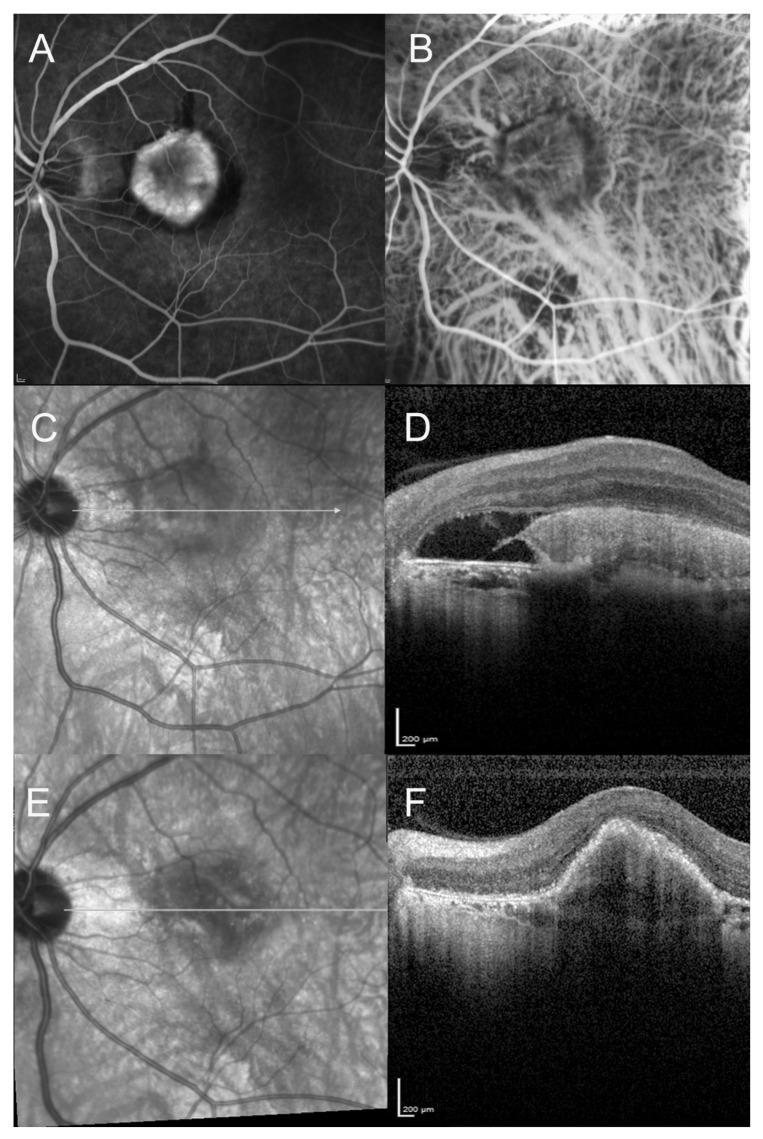
Figure 3.
A 64-year-old man diagnosed with high myopia, presenting with visual acuity loss (20/100). (A–D): Fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green angiography, Infrared reflectance photography, and horizontal Spectral domain optical coherent tomography (SD-OCT) at baseline. Neovascular lesion in a myopic eye with tessellated fundus. SD-OCT scan showing the hyperreflective pre-epithelial neovascular lesion, with subretinal fluid. We can note the disruption of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) layer and the alteration of the photoreceptors layer. (E,F): Infrared reflectance photography and horizontal scan of the SD-OCT at 1-year follow-up, after anti-VEGF therapy. The fibrovascular PED can be observed. Visual acuity improved to 20/40.