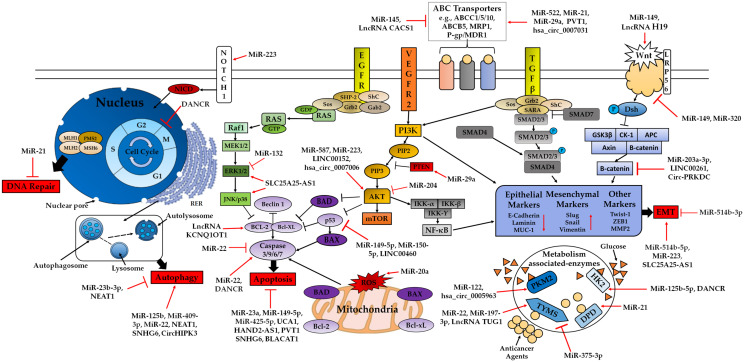
Figure 2.
Classic mechanisms involved in drug resistance (5-FU, OXA, Cisplatin and DOX) in CRC. miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs modulate drug resistance in CRC through different pathways such as the PI3K/AKT, EGFR-RAS-MAPK, WNT/β-catenin, NF-κB, TGF-β and Notch1 signaling pathways, cell death pathways (apoptosis, autophagy), EMT, DNA repair and ABC transporters. Arrows represent activation effect, and the ‘T’ symbols represent inhibition. Arrows and ‘T’ symbols in red represent some of the different ncRNA targets involved in chemoresistance to be discussed in this review. Abbreviations: MLH1: MutL homolog 1; MLH2: MutS homolog 2; PMS2: PMS1 Homolog 2; MSH6: MutS homolog 6; NICD: Notch intracellular domain; RER: Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum; GRB2: Growth Factor Receptor-bound protein 2; SOS: Son of Sevenless; SHP-2: SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2; GAB2: GRB2 Associated Binding Protein 2; SHC: SH2 containing protein; GSK3β: Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β; AKT: Protein Kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; Iκκ: IκB kinase; Dsh: Dishevelled; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; APC: Adenomatous Polyposis Coli; HK2: Hexokinase 2; TYMS: thymidylate synthases; DPD: Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenas; PKM2: Pyruvate Kinase 2; SARA: SMAD anchor for Receptor Activation.