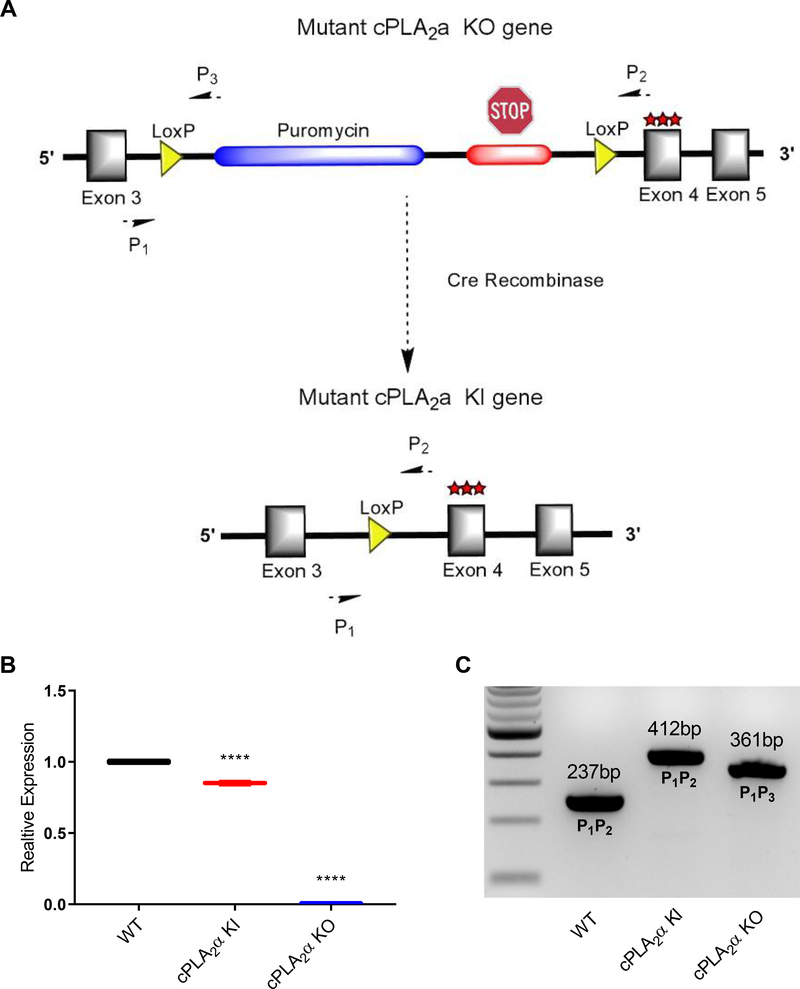
Fig. 1. cPLA2α KI and KO mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the cassette inserted into intron 3 of the endogenous cPLA2a locus. The cassette contains a puromycin resistance gene followed by a premature stop codon flanked by loxP sites. Insertion of the cassette causes cPLA2α KO. The cassette also contains a triple mutation at the C1P binding site (R57A, K58A, R59A) encoded in exon 4. CRE-mediated recombination excises the puromycin resistance gene and premature stop codon, generating KI mice that produce cPLA2α with the mutated C1P binding site instead of wild-type cPLA2α. (B) RNAs from primary dermal fibroblasts from WT, KI, and KO mice were converted to cDNA and used for quantitative PCR analysis using primers specific to cPLA2a. Samples were compared using ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. Data shown are means ± SD, n = 3–6 mice per genotype, ****P< 0.0001. (C) Genotyping of WT, KI, and KO mice using end point multiplex PCR using primers specific for the WT, KI, and KO alleles.