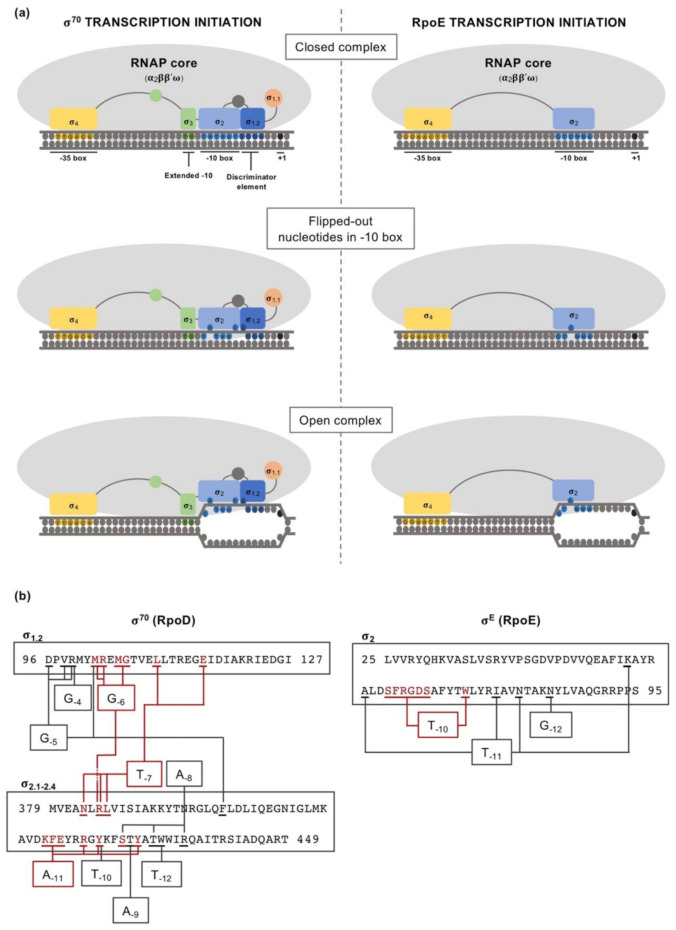
Figure 2.
Comparison between the transcription initiation mechanisms of the primary σ70 factor (RpoD) and the extracytoplasmic function σ factor (ECF) RpoE, from E. coli. (a) Involvement of the different σ factor domains (using the same color code as in Figure 1) in the transcription initiation, emphasizing the differences between the vegetative σ70 factor and RpoE regarding their promoter melting capability. The different isomerization stages from closed complex to open complex are indicated. (b) Schematic of the contacts between -10 box nucleotides and σ2 domain residues for RpoD and RpoE. Residues directly interacting with -10 box nucleotides are underlined. Nucleotides that are flipped-out during transcription initiation and the respective residues that contact them are indicated in red.