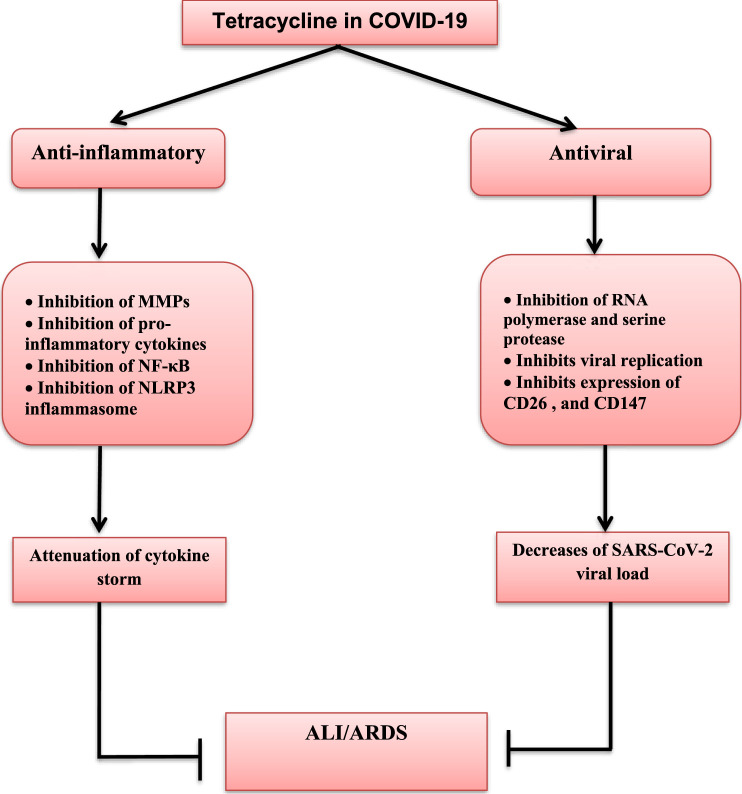
FIGURE 1.
Pleiotropic effects of tetracycline in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Tetracycline has antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects. Antiviral effects of tetracycline are through inhibition of RNA-polymerase and serine protease dependent viral replications, and inhibition of the expression of CD26 and CD147, which are regarded as entry-point for SARS-CoV-2 with subsequent reduction in viral load. Anti-inflammatory effects of tetracycline are through inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), Nod-like receptor pyrin 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines with subsequent attenuation of cytokine storm development. Taken together, both anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects of tetracycline inhibit development of acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19.