FIG 6.
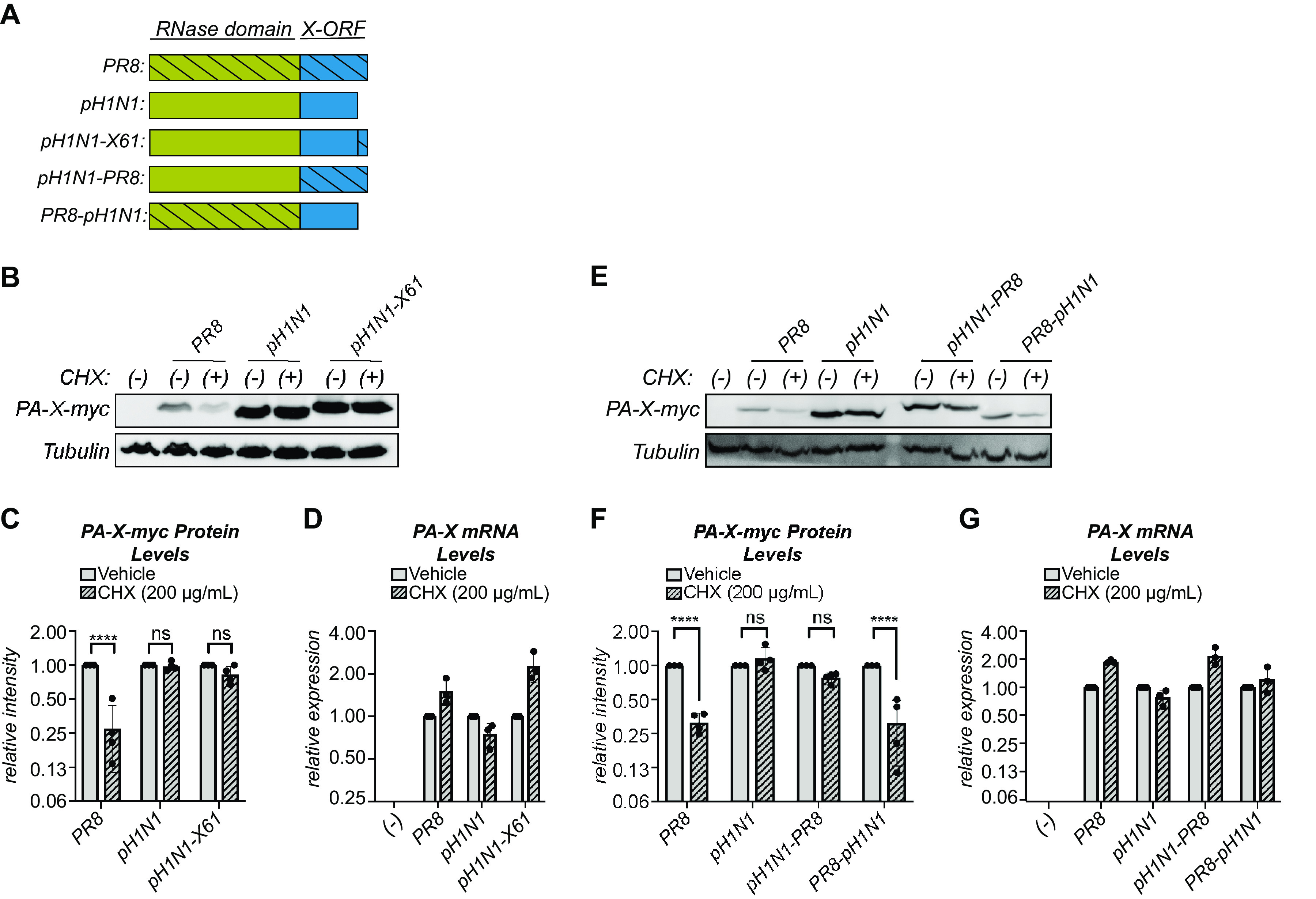
The N-terminal domain of PA-X also has a role in PA-X stability. (A) Schematic diagram of the PR8/pH1N1 PA-X chimeras used. (B to G) Protein and RNA samples were collected from HEK293T cells expressing the indicated catalytically inactive C-terminal myc-tagged PA-X variant 2 hours after treatment with 200 μg/ml of cycloheximide (CHX) to inhibit translation (+) or vehicle control (−). (B, E) Representative Western blot using anti-myc antibodies to detect myc-tagged PA-X and tubulin as a loading control. (C, F) For each replicate, PA-X protein levels were normalized to tubulin protein levels and reported as the amount normalized to vehicle control for each variant. n = 4. (D, G) Levels of PA-X mRNA were measured by RT-qPCR. After normalization to 18S rRNA, levels were plotted as amounts relative to vehicle-treated cells for each variant. n = 3. ****, P < 0.0001; ns, P > 0.05; 2-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple-comparison test.
