FIGURE 1.
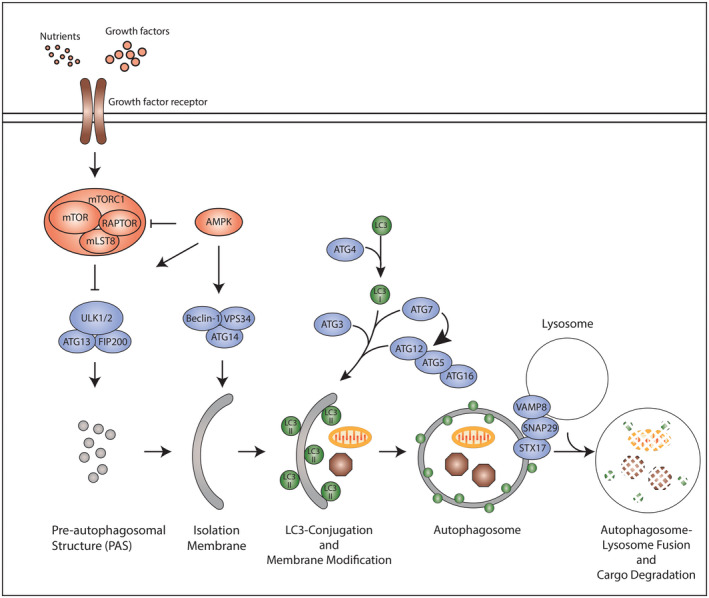
The classical autophagy pathway. Signals are integrated by the core autophagy machinery, which hierarchically regulate individual steps within the autophagy pathway. Formation of the pre‐autophagosomal structure (PAS), the first step in the autophagy pathway, is controlled by the ULK1‐ATG13‐FIP200 kinase complex. Nutrients and growth factors (e.g. amino acids, IGF‐1) trigger signaling through growth factor receptors. Ultimately, these signals converge upon the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) comprised of mTOR, RAPTOR and mLST8, as well as AMPK, which reciprocally modify the ULK complex to regulate its functions in PAS formation. The PAS is subsequently modified by the Beclin‐1‐ATG14‐VPS34 complex to mediate formation of the isolation membrane. Expansion of the isolation membrane is associated with two ubiquitin‐like reactions involving ATG7, ATG5, ATG12, ATG16 and ATG3 which ultimately conjugate phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to microtubule‐associated protein 1 light chain 3 (MAP1LC3B; also known as LC3) and other ATG8 family proteins. LC3‐PE targets LC3 to autophagosomal membranes where it facilitates membrane expansion and cargo sequestration. Finally, the autophagosome double‐membrane is sealed and captured cargo targeted to the lysosome through autophagosome‐lysosome fusion. In this schematic, arrows indicate activating signals, whereas blunt‐end lines represent inhibitory signals
