FIGURE 2.
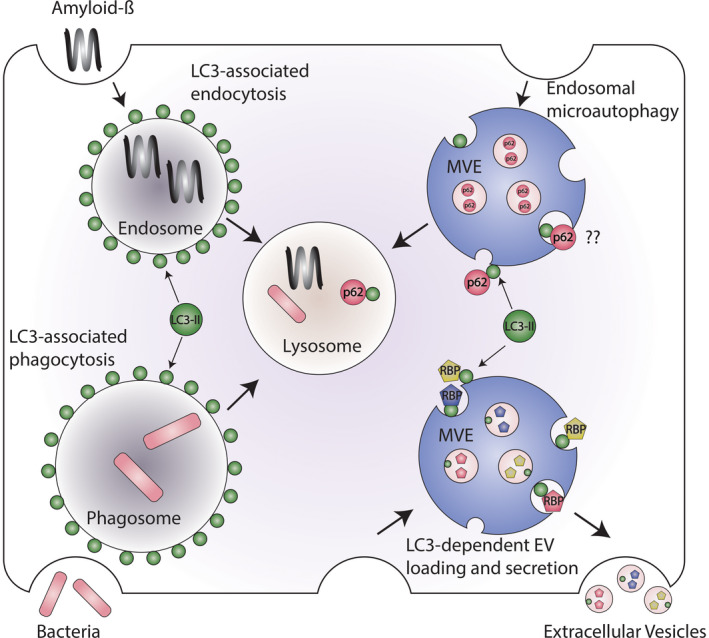
Emerging autophagy‐related pathways that employ LC3‐conjugation to single‐membrane endocytic and phagocytic vesicles. Components of the autophagy conjugation machinery, in addition to regulating classical autophagy, facilitate the delivery of microtubule‐associated protein 1 light chain 3 (MAP1LC3B; also known as LC3) and other ATG8 family proteins to single‐membrane vesicles including phagosomes, endosomes, and multivesicular endosomes (MVEs). During LC3‐associated phagocytosis (LAP) and LC3‐associated endocytosis (LANDO), LC3 delivery to the surface of phagosomes and endosomes, respectively, controls the trafficking and lysosomal degradation of material engulfed from the extracellular space such as bacteria or amyloid‐β. In contrast, LC3 is targeted to discrete subdomains at the limiting membrane of MVEs during endosomal microautophagy (eMI) and LC3‐dependent EV loading and secretion (LDELS), which undergo budding to form small intraluminal vesicles. LC3 facilitates the packaging of RNA‐binding proteins (RBPs) into these intraluminal vesicles, which subsequently are released as extracellular vesicles in the LDELS pathway. LC3 may also mediate the packaging of autophagy cargo receptors such as p62/SQSTM1 into intraluminal vesicles during endosomal microautophagy, but it remains unclear whether such pathways contribute to EV secretion
