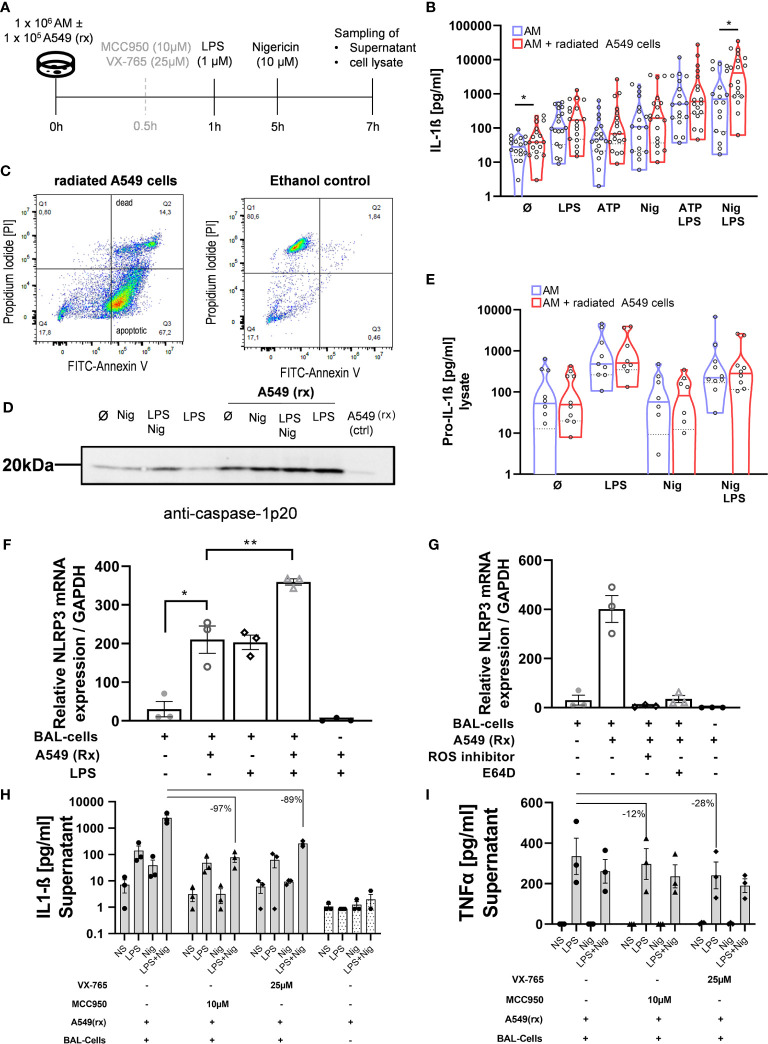
Figure 3.
Efferocytosis of apoptotic alveolar epithelial cells activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in AM. BAL cells were co-cultured with the radiated (rx) A549 cells, and the NLRP3 inflammasome was additionally stimulated (A). A549 cells were radiated with 10 Gy and incubated for 72h, following which the majority of the cells were apoptotic demonstrated by Annexin-V staining (C). There were increased IL-1ß levels with all stimulations, which were statistically significant at baseline and following LPS + Nigericin (Nig) stimulation (B). Increased caspase-1 activation with A549(rx) co-culture was demonstrated by immunoblotting of cleaved caspase-1p20 subsegment (representative blot shown; total of n = 3 immunoblots performed) (D). Pro-IL-1ß levels in cell lysate were not different between BAL cells and BAL cells co-cultured with A549(rx) cells (E). NLRP3 mRNA expression was assessed after 2h of stimulation, w/wo the presence of A549(rx). BAL cells cocultured with A459(rx) expressed NLRP3-mRNA in a similar range as BAL cells stimulated with LPS alone (F). Combined stimulation of LPS and A549(rx) resulted in a marked increase in NLRP3-mRNA expression. The effect on NRLP3-mRNA expression (relative to GAPDH) by efferocytosis was inhibited by either a NADPH-Oxidase inhibitor (ROS-inhibitor; DPI) or a cathepsin inhibitor (E64D) (G). IL-1ß production could be inhibited by inhibition of NLRP3 (MCC950) and also caspase-1 (VX-765) (H), while TNF-α levels were largely retained (I). IL-1ß levels and NLRP3 mRNA levels were compared using unpaired t-tests; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; N.S. non-significant.