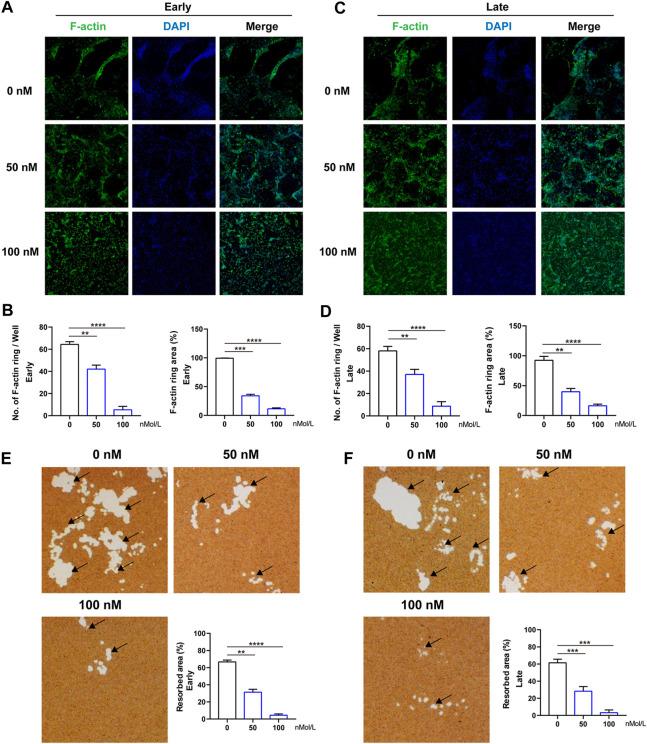
FIGURE 3.
CS-6 suppresses the formation of F-actin ring and bone resorption of OCs. (A) Representative images of F-actin (Green) formed by OCs stimulated by RANKL (50 ng/ml) with indicated concentrations of CS-6 (100 nM) for 5–7 days. (B) The average number and area of F-actin ring. (C) Representative fluorescence images of actin-stained BMM-derived OCs stimulated with RANKL (50 ng/ml) for 3 days prior to indicated concentrations of CS-6 (100 nM). (D) The average number and area of F-actin ring. (E) Representative images of bone resorption pits (white area marked by black arrow) by mature OCs stimulated by RANKL (50 ng/ml) with indicated concentrations of CS-6 (100 nM) for 5–7 days and quantified graph. (F) Representative images of bone resorption pits (white area marked by black arrow) by mature OCs stimulated by RANKL (50 ng/ml) for 3 days prior to indicated concentrations of CS-6 (100 nM) and quantified graph. Values presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.