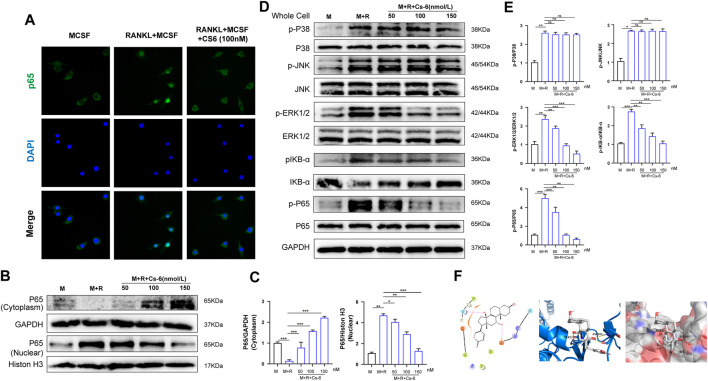
FIGURE 5.
CS-6 attenuated RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and ERK/MAPK signaling pathways. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images regarding the distribution of p65 in BMMs treated by RANKL (50 ng/ml) with or without CS-6 (100 nM) compared to the control group (30 ng/ml MCSF only). (B, C) The protein amount of p65 in cytoplasm and the nucleus was measured by Western blot and quantified, respectively. (D) BMM cells were pretreated with CS-6 (0, 50, 100, and 150 nM) for 3 h prior to stimulation with RANKL for additional 30 min. The total protein amount of the whole cell was determined by Western blot. The key proteins of NF-κB and MAPK pathways were shown. (E) The expression of total proteins was quantified by graphs. (F) (Left) The predicted best binding manner of CS6 in the ATP binding site of IKKβ generated with docking; hydrogen bonds were shown as purple lines. (Middle) Co-crystal structure of the interactions between CS6 and IKKβ; hydrogen bonds were displayed as red lines, and the participating amino acid residues (Thr23 and Asp103) were marked. (Right) MOLCAD representation of the molecular lipophilic potential surface upon the bioactive pose of CS6 in the ATP binding site of IKKβ. The blue denoted the hydrophilic, red for the lipophilic, and gray denoted neutral moiety. Values were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.