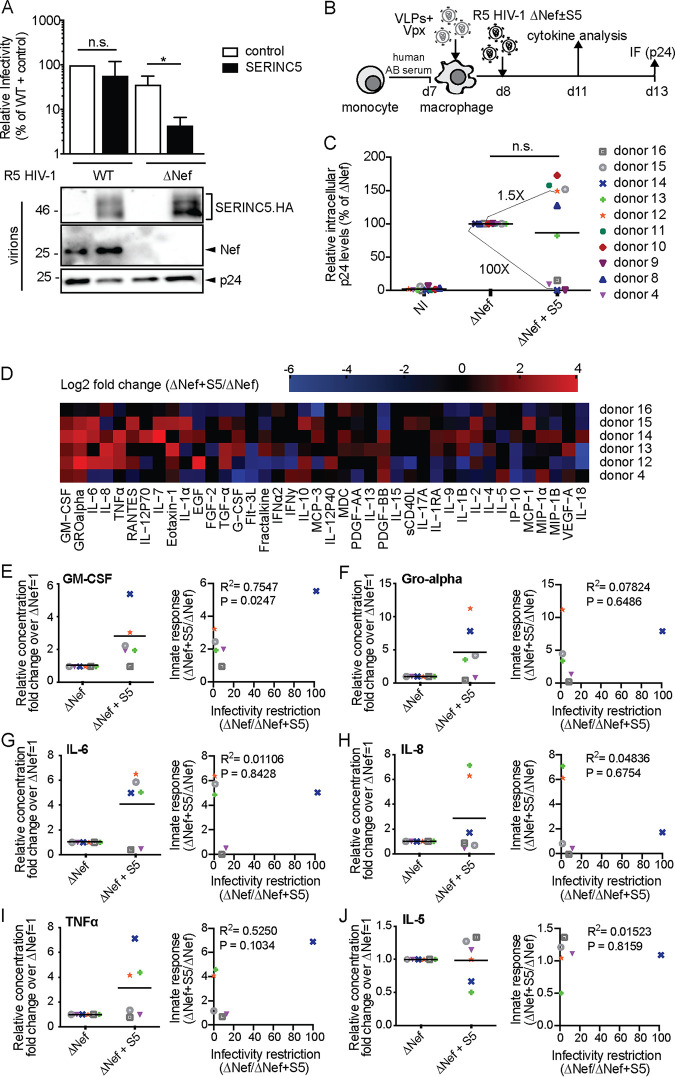
FIG 2.
SERINC5 sensitizes HIV-1 ΔNef particles for increased production of proinflammatory cytokines by monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs). (A, upper panel) Relative infectivity of R5-tropic HIV-1 particles produced in 293T cells analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1A (mean ± SD from three independent virus stocks). (Lower panel) Representative Western blot analysis of these virions for incorporation of SERINC5.HA, Nef, and HIV-1 p24. (B) Schematic of experimental flow. Macrophages were differentiated from monocytes with human AB serum for 7 days. The cells were then transduced with VLPs+Vpx, infected the next day, and analyzed for productive infection (C) or cytokine production from the cell culture supernatant (D) 5 or 3 days p.i., respectively. (C) Relative intracellular levels of p24 as quantified by immunofluorescence (with ΔNef set as 100%). Shown are values of individual infections, with the percentage of p24+ cells ranging from 0.6% to 30% between donors. Data points are from cells of individual donors, with the mean indicated by a black line. The fold changes between the ΔNef ± S5 conditions are indicated for donors 12 and 14 as representatives of donors that display no or pronounced sensitivity to S5-mediated restriction of HIV-1 infectivity. NI, noninfected. (D) Cytokine production of MDMs infected with HIV-1 ΔNef+S5 particles normalized to ΔNef. Data are displayed as log2 fold change, with red, black, and blue, respectively, indicating upregulated, unaltered, or reduced cytokine production. (E to J) Effect of virion incorporation of S5 on the production of individual cytokines (left panels, presented as fold change over ΔNef, set to 1). Shown are data points from cells of individual donors, with the mean value of all donors indicated by a black line. Also shown is Pearson’s correlation between the infectivity restriction by S5 and the S5-mediated induction of each cytokine (right panels). Statistics (Student's t test): n.s., nonsignificant; *, P < 0.05.