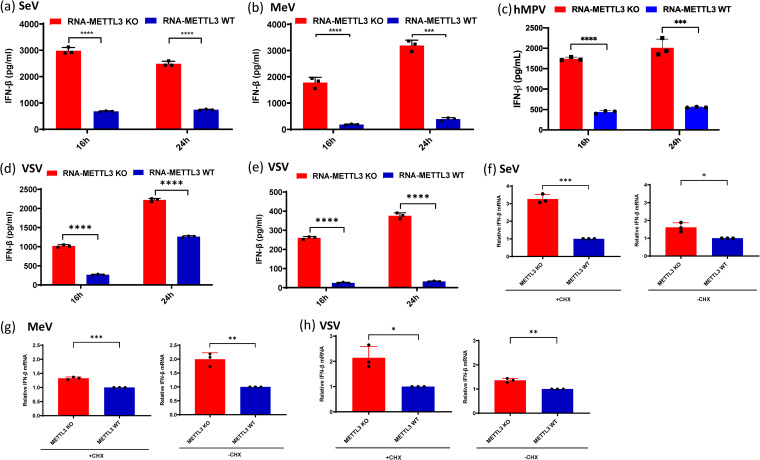
FIG 4.
m6A-deficient viruses and their viral RNAs induce higher type I IFN production. (a to c) Comparison of IFN production triggered by virion RNAs of SeV (a), MeV (b), and hMPV (c) produced from METTL3 KO or WT U2OS cells. A549 cells were transfected with 105 RNA copies of SeV (a), 5 × 106 RNA copies of MeV (b), and 107 RNA copies of hMPV (c), with each virus grown on METTL3 KO or WT U2OS cells. IFN-β production was measured by an ELISA kit at indicated time points. (d to e) IFN-β response in A549 cells transfected with total RNA from VSV-infected cells. Total RNA was extracted from VSV-infected METTL3 KO or WT U2OS cells, and the antigenome/genome was quantified by real-time RT-PCR. A549 cells were transfected with 108 (d) and 107 (e) copies of viral RNA. IFN-β was measured by ELISA at indicated time points. (f to h) IFN-β mRNA level in A549 after viral infection with or without cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. A549 cells were treated for 1 h with 0 or 50 μg/ml CHX and then infected with either SeV (f), MeV (g), or VSV (h) grown in METTL3 KO U2OS or WT U2OS cells. Total RNA was extracted from virus-infected cells, and IFN-β mRNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR. The relative mRNA level between METTL3 KO- and WT U2OS cell-derived viruses was calculated. The data shown are the mean ± SD from n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by two-sided Student's t test: *, P < 0.5; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.