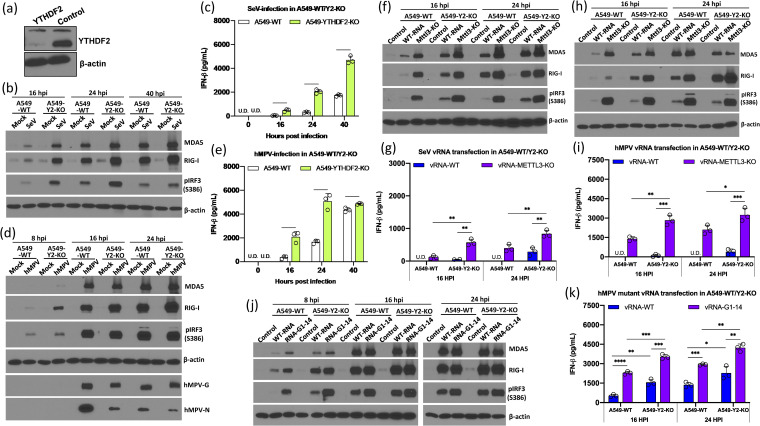
FIG 9.
YTHDF2 is essential for suppression of the IFN signaling pathway. (a) Western blot analysis of YTHDF2 in YTHDF2 knockout A549 cells and control sgRNA-treated A549 cells. (b) SeV infection induces a higher IFN signaling pathway in YTHDF2 knockout A549 (A549-Y2 KO) cells compared to WT A549 cells. Confluent cells were infected by SeV at an MOI of 1.0, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting at the indicated time points. (c) IFN production in WT and YTHDF2 knockout A549 cells upon SeV infection at an MOI of 1.0. (d) hMPV infection induces a higher IFN signaling pathway in A549-Y2 KO cells compared to A549 WT cells. Cells were infected by hMPV at an MOI of 1.0. (e) IFN production in WT and YTHDF2 knockout A549 cells upon hMPV infection at an MOI of 1.0. (f) Comparison of IFN signaling pathways in A549-Y2 KO cells and A549 WT cells upon transfection of equal amounts (106 RNA copies) of WT SeV RNA and m6A-deficient SeV RNA. (g) IFN production in WT and YTHDF2 knockout A549 cells upon SeV RNA transfection (106 RNA copies). (h) Comparison of IFN signaling pathway in A549-Y2 KO cells and A549 WT cells upon transfection of equal amounts (106 RNA copies) of WT hMPV RNA and m6A-deficient hMPV RNA. (i) IFN production in WT and YTHDF2 knockout A549 cells upon hMPV RNA transfection (106 RNA copies). (j) Comparison of IFN signaling pathways in A549-Y2 KO cells and A549 WT cells upon transfection of equal amounts (106 RNA copies) of WT hMPV RNA and hMPV G1-14 RNA. (k) IFN production in WT and YTHDF2 knockout A549 cells upon WT hMPV RNA and hMPV G1-14 RNA transfection (106 RNA copies). The Western blots shown are the representatives of three independent experiments. The interferon data shown are the mean ± SD from n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by two-sided Student's t test: *, P < 0.5; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.